
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Navigating India's Capital
Markets
Evolving Horizons


Message
Capital markets play a crucial role in fuelling economic growth and development in the country. The Indian capital
market is poised for continued growth, driven by a young and aspirational population, rising incomes, and increasing
financial literacy.In the economy, this vibrant and dynamic marketplace not only generates wealth but also provides an
avenue for individuals and companies to raise funds for productive purposes, fostering entrepreneurship and
investment. The capital market also provides options for risk diversification for investors, leading to enhanced overall
financial inclusion and economic stability.
To enhance investor confidence and attract more participants, the Indian government has introduced measures such
as simplified regulations, improved corporate governance practices, and greater transparency in reporting standards.
Initiatives taken by the government are crucial to enhance the overall efficiency, security, and effectiveness in the
operations. These reforms are not just incremental changes; they are transformative leaps that will unlock India's true
potential. While the strength and accessibility of Indian markets have been ensured by regulatory framework and
technological advancements, it is crucial to further strengthen the regulatory environment, expand market
participation, and promote financial literacy to foster a thriving and inclusive capital market in India.
Viksit Bharat @2047 aims to transform India into a developed economy focussed on strengthening the capital markets,
technology, infrastructure, etc. that promote the achievement of this goal. Widening the reach of the capital markets will
help in smoothening the business functions as it enables them to have a wider and more accessible market to pool
funds, increasing market liquidity and thus promoting ease of business. The vision of a developed India also intends to
deepen financial inclusion in the economy, by making necessary amendments in the key sectors and hence catering
towards enhanced knowledge about the capital markets and their uses so that even small and medium enterprises can
invest in such markets. With promising economic indicators and sustainable development, we firmly believe that India
will emerge as a developed economy with thriving capital markets by the time we celebrate our 100 years of
independence.
The role of Capital market in meeting India's long-term funding requirements assumes huge significance. In this context,
ASSOCHAM jointly with Resurgent India Ltd. has come out with this Report on the subject highlighting various aspects of
the capital market. We hope that the contents of the Report will provide valuable insights to policymakers and industry
stakeholders and the deliberations at the summit will help in laying the roadmap for future growth and development of
the Indian capital market.
Deepak Sood
Secretary General, ASSOCHAM
Deepak Sood

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
India's equity market, now the 5th largest globally by market capitalization, has seen an exponential increase in
retail investor participation, a testament to the burgeoning confidence in India's financial policies and market
mechanisms. The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) now boasts the highest number of listed companies worldwide,
highlighting the depth and diversity of India's corporate sector. This growth has been fueled by relentless
innovations and regulatory fortifications by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which has been
pivotal in enhancing market transparency and investor protection. India's transition to the T+1 settlement cycle,
ahead of many developed and emerging economies, exemplifies the market's efficiency and its forward-
thinking approach to financial transactions.
The debt market presents a nuanced narrative. While the government securities (G-Sec) market demonstrates
robust liquidity and an expanding investor base, the corporate bond market remains relatively underexplored. It
has had to contend with a blend of regulatory constraints and operational complexities. However, recognizing
these challenges, SEBI and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have embarked on a commendable journey to
invigorate this sector. Introducing market makers to enhance liquidity, and the push for a uniform valuation
framework, will likely lead to a strategic shift towards a more dynamic and inclusive debt market.
This report is a compendium of insights and forward-looking statements. It's crafted for stakeholders across the
spectrum – from policy-makers and global investors to financial enthusiasts and the academic community –
offering a granular analysis of current trends, regulatory advancements, and the potential trajectory of India's
financial markets.
As we look towards the future, it's clear that India's financial markets are not just growing in size but are becoming
more sophisticated, inclusive, and aligned with global best practices. This evolution is a beacon of India's broader
economic aspirations and its unwavering commitment to becoming a central hub in the global financial
ecosystem.
Message
Jyoti Prakash Gadia
Managing Director, Resurgent India Ltd
Jyoti Prakash Gadia

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SR.NO CHAPTERS PAGE
1 Executive Summary 6
2
Contemporary Landscape of
Indian Capital Markets
9
3
Government Initiatives and Regulatory
Environment
19
4
5
6
Capital Markets for Indian SMEs
A Comparative Analysis
Key Findings
22
25
27

Executive Summary
Over the past two decades, India's financial markets have matured and grown to find a place amongst the
largest markets. As of December 2023, our market cap has hit a remarkable $4.379 trillion, placing it fifth among
the top 10 highest-valued countries worldwide.
The advent of digital platforms such as Zerodha Kite, Upstox Pro, Angel Broking Mobile App, Groww, ICICI Direct,
HDFC Securities Mobile Trading, Kotak Stock Trader, 5paisa Mobile App, Sharekhan App, Motilal Oswal MO Investor
App and Edelweiss Mobile Trader has catalysed a significant increase in retail investor participation in financial
markets. While the echoes of pandemic-induced uncertainties linger they have not dampened the enthusiasm
of market participants. Concurrently regulatory bodies are proactively instituting reforms designed to bolster the
transparency and stability of the financial markets promising a more robust framework for investors moving
forward.
India's equity market has evolved to become a benchmark of development and innovation, aligning itself with
global standards. It now proudly stands as the 5th largest in the world in terms of market capitalization. The
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), a flagship Indian exchange, is recognized for having the highest number of listed
companies worldwide. This growth is a testament to India's commitment to technological advancements and
regulatory enhancements. The surge in retail investor participation is particularly noteworthy, thanks to the
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)'s efforts towards investor education and protection. India's
pioneering move to the T+1 settlement cycle exemplifies its leadership in market practices, setting a precedent
for both developed and emerging markets.
The landscape of India's debt market, while robust for government securities in liquidity and investor
engagement, reveals the corporate bond segment's untapped potential. The corporate bond market faces
challenges including a preference for private placements, limited retail engagement, and regulatory and
operational complexities that deter risk-taking. Despite India boasting a large economy and a substantial
domestic government bond market, it remains excluded from major global government bond debt indexes. As a
result, it misses out on the substantial portfolio inflows typically associated with inclusion in these indexes. This
exclusion hinders India's ability to leverage its economic size and market potential to draw significant foreign
investment and diversify its funding sources. Expanding domestic financial markets will lead to a more efficient
distribution of investment funds and improved resource pricing, simplifying the execution of national agendas
for privatization and innovation.
A large share of Indian household income goes into savings. While more than half of it goes into physical assets
like gold and housing the rest goes into financial assets which are then available for investments by companies
and governments.
Capital formation in India involving public and private sectors witnessed an investment boom from 2004 to 2008
CHAPTER 1
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
6

India's Vision 2047 encompasses a broad and ambitious plan to transform the nation into a developed economy,
emphasizing significant advancements across various sectors, including capital markets, infrastructure,
technology, and social welfare. This vision aligns with the goal of creating a $30 trillion economy by leveraging
India's demographic dividend, technological innovation, and sustainable development practices. One of the key
aspects of this vision is the development and strengthening of capital markets as a crucial element for mobilizing
resources to fund infrastructure and foster economic growth.
With Vision 2047's emphasis on infrastructure, technology, and social welfare, there's a critical need to expand
and deepen capital markets. This involves introducing more diversified financial instruments, India’s inclusion in
a greater number of global indices, and enhancing market liquidity, thereby making it easier for businesses and
projects aligned with Vision 2047's goals to access funding. As of the end of 2022, foreign investors held less than
1% of the total outstanding government bonds. Greater influx of foreign investment into India's public sector will
unlock substantial resources and significantly bolster the capital accessible for the nation's economic
expansion. Broader index inclusion could help raise foreign involvement in India's government bond market to
10% from the existing 0.9% (source: Institute of International Finance).
Key Aspects of Vision 2047 and Capital Formation
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
with the Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) to GDP ratio peaking at 34.7% in 2008. Following the global financial
crisis this ratio moderated showing a downward trend until 2017 and slightly recovering in 2018.
Recent trends indicate a decline in household financial savings to 5.1% of GDP in FY 2023 from 7.2% in FY 2022
alongside an increase in financial liabilities from 3.8% to 5.8% of GDP. Despite these challenges the national
initiative ensuring universal access to bank accounts has established a robust framework to potentially elevate
financial savings.
7

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Fostering Innovation and Entrepreneurship
A key aspect of capital formation in the context of Vision 2047 is the support for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Capital markets can provide the necessary risk capital for startups and innovative projects that contribute to
technological advancements and sustainable development. By creating a favorable regulatory and investment
environment, India can attract more venture capital and private equity investment, essential for nurturing a
culture of innovation.
Strengthening Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) have been identified as a crucial mechanism for accelerating infrastructure
development, a major pillar of Vision 2047. Capital markets can support PPPs by providing innovative financing
solutions, such as infrastructure investment trusts (InvITs) and municipal bonds. These instruments enable
private investment in public projects, ensuring efficient capital utilization and sharing of risks and rewards
between the public and private sectors.
Promoting Sustainable and Green Finance
Aligned with Vision 2047's focus on sustainable development, there's a growing importance of green finance
within capital markets. Encouraging the issuance of green bonds and other sustainable financial products can
direct capital towards environmentally friendly and sustainable projects. This not only supports India's
commitment to environmental sustainability but also opens up new investment avenues for socially responsible
investors.
Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Capital formation in the context of Vision 2047 also involves enhancing financial inclusion. By leveraging
technology to broaden access to capital markets, India can ensure that a larger segment of the population
benefits from economic growth. This includes facilitating small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) access to
public markets and providing retail investors with opportunities to invest in government and corporate bonds.
The vision also emphasizes ramping up government spending on education to global standards and unlocking
the healthcare services sector. These efforts aim to build human capital capable of supporting India's ambitious
economic growth and development goals. To support the vision of a tech-driven economy, three centres of
excellence for artificial intelligence are planned to be established in prestigious educational institutions. This
aligns with the goal of making AI in India and making AI work for India, fostering innovation and technological
advancement. India's Vision 2047 incorporates a strong emphasis on sustainable growth, including initiatives
like the National Hydrogen Mission aimed at making India a hub for green hydrogen production. This reflects a
broader commitment to green growth and climate action.
8

Contemporary Landscape of Indian Capital Markets
The 2024 outlook for the Indian stock market appears highly favourable, driven by robust economic growth,
strong corporate earnings and increased domestic investment. The optimism stems, in good measure, from
India's status as the fastest-growing major economy with growth expected to surpass at least 6% in the
foreseeable future, bolstering domestic equities. The surge in young Indian investors and mutual fund accounts
further supports this trajectory.
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) have been instrumental in shaping
India's market dynamics, demonstrating worldwide confidence in its economic potential and significantly
contributing to market liquidity and overall sentiment. The latest figures indicate a strong foreign investment
presence in India's financial markets, showcasing both Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Foreign Portfolio
Investors (FPIs)'s active participation. This trend of substantial investments indicates continued confidence
among foreign investors in the Indian market's potential, despite some instances of selling in September 2023.
These investments reflect a broad-based endorsement of India's economic and market fundamentals,
suggesting that despite occasional market volatilities, the overall investor sentiment towards India remains
positive. The inflows from FII and FPI investments are crucial for India's financial market liquidity and can
significantly impact market movements and the rupee's exchange rate against other currencies. The Indian
government's efforts to liberalize regulations for foreign capital have significantly increased the attractiveness of
the Indian market for global investors. This regulatory liberalization, along with improved financial awareness
and better access to financial services, has notably influenced the influx of foreign institutional investments.
CHAPTER 2
Initial Public Offerings in India
The IPO market in India has experienced remarkable growth expanding from US$22 billion in 2021 to US$3.26
trillion in 2023. This surge can be attributed to a strong domestic capital market, a sizable retail investor base, and
an adaptable regulatory framework overseen by SEBI. The rise in IPO activity not only confirms India's status as a
major investment hub but also highlights the efficacy of SEBI's regulatory measures in fostering a fair and
transparent market environment. India's IPO landscape has been bustling with companies from various sectors
making their public debut.
In December 2023, Muthoot Microfin Limited, Inox India Limited, and India Shelter Finance Corporation Ltd came
up their IPOs. Notable companies like Ixigo, VLCC Healthcare, GPT Healthcare, Penna Cement, and Snapdeal are
poised to enter the public market aiming for significant capital raises through their IPOs. Additionally, firms such
as Rashi Peripherals, Platinum Industries, Exicom Tele-Systems, and Entero Healthcare Solutions are scheduled to
launch their IPOs covering a diverse range of industries from technology to healthcare.
The diversity of companies entering the public market reflects the vibrancy and growth potential of the Indian
economy. The Indian IPO market offers a mix of mainline and SME offerings accommodating a broad spectrum of
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
9

Recent Developments
SEBI has implemented several regulatory revisions aimed at bolstering transparency and safeguarding investor
interests within the capital markets. Notably the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) (Amendment) Regulations,
2024 have introduced notable modifications such as mandating Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) to maintain
investments in dematerialized form unless certain exceptions apply with the objective of augmenting
transparency in investment holdings. Moreover, the amendment requires AIFs to designate a custodian for
securities safekeeping with specific guidelines outlined for custodians affiliated with the AIF's Sponsor or
Manager thereby ensuring autonomy and clarity in the custodial process.
Equity, commodities and forex derivatives segment remain the most vibrant parts of the Indian capital markets
and draws the attention of both retail and institutional participants. Over the span of three years leading up to
March, retail investor involvement in India's equity derivatives market surged by 500%.
According to the most recent data available, derivatives trading comprising futures and options commands a
significant share of trading volume in Indian capital markets with options trading alone representing 98% of all
derivatives contracts traded in India. This substantial presence of derivatives trading underscores the depth of
the market and the active involvement of both retail and institutional investors in these segments. The regulatory
authority, SEBI maintains continuous oversight of this activity to uphold market stability and safeguard investor
interests.
However heightened activity has also raised concerns among regulators regarding potential risks for retail
investors amidst market volatility. A notable proportion of individual traders incurred losses prompting the SEBI to
contemplate measures aimed at limiting retail investors' exposure to derivatives based on their wealth.
In like manner, the corporate debt market experienced expansion as companies sought funds through bonds
and debentures. In 2024, India's debt market is anticipated to remain an attractive investment avenue with
wealth managers expressing optimism about the country's economic prospects despite macroeconomic
challenges. Positive sentiments surround fixed income investments anticipating capital gains from expected
rate cuts in both India and the U.S. Additionally, there is considerable interest in alternative investments like
private credit and real estate funds. This outlook reflects a general sentiment that although specific sectors may
exhibit some overvaluation, the overall valuation landscape in India is somewhat stretched but not overly
concerning.
Additionally, mutual funds continued to be a favoured investment choice among retail investors offering a
variety of schemes and options. India's mutual fund industry has witnessed significant growth driven by factors
such as increased retail participation, growing recognition of mutual funds as viable investment vehicles and
technological advancements facilitating easier access to mutual fund investments. Key trends observed in
recent years expected to persist into 2024 include a surge in systematic investment plan (SIP) contributions,
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
10
investors seeking portfolio diversification or exposure to new markets. SEBI has been proactively engaged in
fostering retail investment by streamlining the IPO application process and promoting investor education. The
proliferation of demat accounts in India, a key metric reflecting retail involvement, has witnessed substantial
growth, surpassing notable benchmarks.

India's equity market has not evolved in isolation but as part of a global financial ecosystem increasingly
interconnected and influenced by technological advancements. The introduction of electronic trading systems
in the 1990s marked a pivotal moment, enhancing market accessibility and efficiency. Similarly, the global trend
towards dematerialization facilitated smoother, more secure transactions, aligning India with international
standards.
Moreover, the liberalization of the Indian economy in the early 1990s played a crucial role in attracting foreign
investments, leading to a more integrated market. The gradual relaxation of foreign direct investment (FDI)
norms has further bolstered this integration, making India an attractive destination for global investors.
Key Market Segments: Challenges and Recommendations
Equities: A Global Context
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
11
heightened interest in debt and hybrid funds amid market volatility, and a rise in investments in sector-specific
and thematic funds.
The notable expansion in Assets under Management (AUM) within India's mutual fund sector reflects increased
investor confidence. Asset Management Companies (AMCs) have widened their portfolio offerings to
encompass a diverse array of mutual fund landscape into a robust and vibrant segment including thematic,
sector-focused, ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) funds and funds with specific maturity targets.
There has been a significant rise in the utilization of digital channels for mutual fund investments facilitated by
web platforms and mobile applications thereby extending reach to a broader investor base.

While platforms like the SME exchange are steps in the right direction, more innovative policies could further
boost SME participation. For instance, offering tax incentives for investments in SMEs or creating a dedicated fund
to provide financial support could encourage more listings and investment in this segment.
Policy Innovations for SMEs
Debt Markets
The potential of India's debt market, particularly the corporate bond segment, is immense, yet unlocking this
potential requires overcoming significant hurdles. The G-Sec (Government Securities) market in India is
comparatively more developed, serving as a benchmark for risk-free rates and playing a crucial role in the
financial system. However, the corporate bond market lags in development, facing challenges such as limited
liquidity, a narrow investor base, and regulatory constraints. Addressing these issues can catalyze the market's
growth, providing a vital financing avenue for businesses and contributing to economic development.
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Innovations such as algorithmic trading and artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance market efficiency and
transparency. However, to fully leverage these technologies, there needs to be a regulatory framework that
ensures fair practices and minimizes systemic risks. Furthermore, blockchain technology could revolutionize
trade clearing and settlement processes, making them more secure and efficient.
Fostering Innovation and Technology in Trading
Path Forward
The use of big data analytics in market surveillance can be a game-changer in identifying and mitigating risks
associated with market manipulation and fraud. By analyzing trading patterns in real-time, regulators can
detect anomalies that may indicate manipulative practices, thereby enhancing market integrity.
Leveraging Big Data for Market Surveillance
Efforts to educate investors should go beyond traditional methods and leverage digital platforms to reach a
wider audience. Initiatives like gamified learning experiences and mobile applications that offer simplified
investment advice could bridge the financial literacy gap. Furthermore, promoting financial inclusion by easing
access to investment opportunities for underrepresented sections of the population could contribute to more
balanced market growth.
Inclusive Growth and Financial Inclusion
While market volatility and corporate governance issues are well-acknowledged challenges, deeper structural
issues also merit attention. For instance, the skewed market capitalization, where a few large-cap stocks
dominate trading volumes, reflects underlying issues in market breadth. This concentration risk can exacerbate
market volatility and limit the market's ability to function as a barometer for the broader economy.
Another nuanced challenge is the digital divide and financial literacy gap, which affects the equitable
participation of the investor base. While urban areas have seen a surge in investor participation, rural areas
remain underrepresented, partly due to limited access to digital platforms and financial education.
Challenges: Beyond the Surface
12

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Overcoming Challenges
The Indian financial system's heavy reliance on bank financing, especially for infrastructure projects, points to a
deeper issue of risk aversion and a lack of market mechanisms to effectively price and manage credit risk.
Developing a more vibrant corporate bond market could provide an alternative financing route, potentially
lowering the cost of capital and spreading risk more broadly across the economy.
Bridging the Gap Between Bank Financing and Bond Financing
While simplifying issuance norms and reducing compliance costs are critical steps, regulatory reforms could
also include creating a more favorable tax regime for bond investments and introducing more flexible credit
rating criteria for issuers. This could help smaller and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) access the bond market,
diversifying the issuer base.
Regulatory Reforms: Beyond Simplification
Enhancing liquidity in the secondary market is vital for the growth of the corporate bond market. Beyond
traditional measures like market-making schemes, leveraging financial technology (FinTech) can play a
transformative role. For instance, blockchain technology could streamline the issuance and settlement process,
reduce costs, and increase transparency. Similarly, AI and machine learning could enhance credit risk
assessment, making it easier for investors to evaluate bond investments.
Market Infrastructure Development: Leveraging Technology
Allowing greater participation from foreign and institutional investors is crucial. However, this should be coupled
with strategies to broaden the domestic investor base. Innovative financial instruments such as bond ETFs
(Exchange-Traded Funds) and infrastructure investment trusts (InvITs) can make bond investments more
accessible to retail investors. Moreover, developing a credit default swap (CDS) market could mitigate credit risk
concerns, making corporate bonds more attractive to a wider array of investors.
Expanding the Investor Base: Strategic Approaches
13

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Widening the Derivatives Market
India's derivatives market, a crucial component of the financial ecosystem, has seen remarkable growth,
especially in the equity derivatives segment. This growth reflects an increasing appetite among investors for
sophisticated financial instruments that can hedge against market volatility. However, the journey ahead
involves navigating through complexities to unlock further growth. This includes expanding product diversity,
simplifying regulatory frameworks, and enhancing investor education to ensure a deeper understanding of
these complex instruments.
The introduction of a broader array of derivative products such as commodity derivatives, credit derivatives, and
even weather derivatives could significantly enhance the market's utility and attractiveness. For instance,
commodity derivatives can provide a critical hedging tool for stakeholders in India's vast agricultural sector,
offering protection against price volatility. Credit derivatives, on the other hand, can offer new ways to manage
credit risk, especially valuable in a growing economy with diverse credit profiles.
Innovations such as structured derivatives, which cater to specific investor needs by combining various
underlying assets, could also add depth to the market. These products can meet the sophisticated hedging and
investment strategies of institutional investors while potentially opening new avenues for retail investor
engagement through simplified structures.
Product Innovation: Beyond Equity Derivatives
Pathways to Growth
Promoting the issuance of green bonds and bonds financing sustainable projects could tap into the growing
global demand for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments. This not only provides a new
avenue for issuers but also aligns India's debt market development with global sustainability goals.
Encouraging Green Bonds and Sustainable Financing
A corporate bond guarantee mechanism, possibly backed by the government or a consortium of banks, could
mitigate the perceived risk of corporate bond investments. This would encourage more conservative investors,
such as pension funds and insurance companies, to allocate a portion of their portfolios to corporate bonds.
Developing a Corporate Bond Guarantee Mechanism
Fostering an ecosystem that encourages financial innovation can lead to the development of new financial
products and platforms that enhance market efficiency and accessibility. Regulatory sandboxes, where new
financial products and technologies can be tested under relaxed regulatory conditions, could encourage
innovation in the debt market space.
Creating an Ecosystem for Financial Innovation
A corporate bond guarantee mechanism, possibly backed by the government or a consortium of banks, could
mitigate the perceived risk of corporate bond investments. This would encourage more conservative investors,
such as pension funds and insurance companies, to allocate a portion of their portfolios to corporate bonds.
Developing a Corporate Bond Guarantee Mechanism
14

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Simplification and Education: Demystifying Derivatives
The complexity of derivatives often acts as a barrier to entry for a significant portion of potential market
participants. Streamlining regulatory processes to make it easier for both issuers and investors to engage with
derivative products is crucial. This simplification must be accompanied by robust educational initiatives aimed
at demystifying derivatives for retail investors. Such initiatives could include interactive webinars, virtual trading
simulations, and comprehensive guides that cover the basics of derivatives trading, risk management, and
strategic applications.
Strengthening risk management frameworks is essential to safeguard against systemic risks, particularly as the
derivatives market grows and diversifies. This involves not only the implementation of robust regulatory
measures and oversight mechanisms but also encouraging the adoption of advanced risk management
practices among market participants. For instance, the use of AI and machine learning in monitoring market
patterns and risks can offer more nuanced insights into potential vulnerabilities, enabling preemptive actions to
mitigate risks.
Risk Management: A Foundation for Innovation
An integrated approach that considers the interdependencies between the equity, debt, and derivatives
markets is essential for a cohesive financial market development strategy. This involves:
• Coordinated Regulatory Reforms: Regulatory harmonization across different segments of the financial
market is crucial. A unified approach by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), RBI (Reserve Bank of India),
and the Ministry of Finance can ensure that reforms are aligned and mutually reinforcing, promoting a balanced
market development.
• Infrastructure and Technological Advancements: The role of technology in enhancing market
infrastructure cannot be overstated. Advanced trading platforms, real-time settlement systems, and state-of-
the-art cybersecurity measures can significantly improve efficiency, accessibility, and confidence in the
financial markets.
Integrating Strategies for Financial Market Development
15

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
The theme of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) has not only cemented its relevance across the
globe's capital markets but has also started sprouting within India, indicating a shift towards more sustainable
investment practices. The projection for global ESG Assets Under Management (AUM) is set for a robust increase
moving from approximately USD 20 trillion in 2021 to an estimated USD 34 trillion by 2026 which would represent
about 22% of the total AUM. This growth is not just numerical; it's reflective of a deeper trend where companies
prioritizing ESG are delivering superior margins and returns. This edge is largely due to more favourable capital
costs with ESG indices worldwide also outperforming traditional market benchmarks underscoring the financial
viability of sustainable investing.
Meanwhile challenges in China, including issues with reporting standards, labour law compliance, the impacts of
its zero-Covid policy and various socio-economic concerns have somewhat stifled its ESG performance. This
situation opens the door wider for India to step in as a more attractive destination for ESG-focused investments
from around the globe. Looking ahead ESG is poised to become a cornerstone in the decision-making process
within Indian capital markets and is projected to account for approximately 34% of the country's total domestic
AUM by 2047. This anticipated growth is likely to be fueled not only by the advent of new ESG assets emerging from
sectors like Renewable Energy, Electric Vehicles (EV), Green Hydrogen, and Climate Tech but also through the
reclassification of existing assets not previously identified under the ESG umbrella, marking a significant evolution
in how investments are viewed and valued in India's financial landscape.
The role of ESG factors in the Indian capital market has been gaining significant momentum with a strong focus on
non-financial reporting and sustainability practices. The evolving ESG landscape in India highlights the increased
demand for transparency and accountability from companies regarding their ESG initiatives. This shift is largely
driven by stakeholders’ expectations and the understanding that addressing ESG issues is crucial for long-term
sustainability and resilience in the face of challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic.
A key development in this area is the SEBI initiative to enhance ESG disclosures and practices among Indian
companies. This model includes Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) under environmental, social and governance
attributes for reasonable assurance focusing on aspects such as water footprint, gender diversity, greenhouse
gas footprint and employee well-being and safety.
The push towards ESG reporting in India reflects a broader trend of integrating ESG factors into corporate
decision-making and reporting processes. Companies are now expected to align their sustainability
interventions with leading ESG reporting standards and integrate ESG analytics to provide a comprehensive
picture of the organization's value creation. This integration is crucial for attracting and retaining investors who are
increasingly considering ESG factors in their investment decisions. The Task Force on Climate-related Financial
Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations have also been highlighted as a comprehensive framework for companies
to report climate risks and opportunities aiding investors in analysing potential financial impacts due to climate
change.
The effect of the new ESG framework extends beyond the listed companies impacting supply chains and smaller
enterprises. It emphasizes the importance of ESG footprints across a company's supply chain urging listed
companies to support their partners in developing processes for ESG disclosures. This approach aims to provide a
Role of Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) in Indian Capital Market
16

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
The Indian capital markets are undergoing transformative changes, driven by data and technology trends that
are reshaping the landscape for investors, corporations, and regulators. The confluence of rising interest rates,
increased ESG reporting and investing, a booming insurance sector, and significant investments in technology to
harness data, points to a rapidly evolving market environment.
One of the notable trends is the shift towards digitalization, prompted by the growing competitiveness in the
financial industry. Financial institutions are increasingly partnering with fintech firms to digitize their operations
to boost operational agility and remain competitive. This evolution is essential for staying relevant in the modern
era, with more banks and financial institutions digitizing their operating models to stay ahead of the competition.
India needs to focus on the interplay of data and technology, considering the unique dynamics of the Indian
economy, regulatory environment, and technological adoption trends.
The integration of blockchain, cybersecurity enhancements, Regulatory Technologies (RegTech), cloud
computing, and fintech collaborations within India's capital markets marks significant progress. However,
substantial efforts are still required to fully leverage these technologies for market advancement:
Data and technology for new age market challenges
While blockchain's potential to transform clearing and settlement processes is recognized, its widespread
adoption across India's capital markets remains in its infancy. More initiatives and pilot projects are needed to
test blockchain's efficacy in real-world scenarios, ensuring that the technology can significantly reduce
settlement times and enhance security and transparency while addressing counterparty risks effectively.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security and Transparency
17
complete picture of ESG risks and impacts thereby enhancing transparency and mitigating green washing risks.
India's evolving ESG landscape represents a significant shift towards sustainable and responsible business
practices driven by regulatory changes, investor demand and a broader societal recognition of the importance of
ESG factors. Companies that adapt to these changes and effectively integrate ESG principles into their operations
are likely to benefit from increased investor interest, better risk management, and a more sustainable growth
trajectory.

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
RegTech's potential to streamline compliance with complex regulatory requirements is clear, yet the full
deployment of automated compliance tools remains to be achieved. The capital markets ecosystem needs to
embrace these technologies more broadly, ensuring that AI-powered tools are effectively monitoring
transactions and identifying non-compliant activities.
Regulatory Technologies (RegTech) for Compliance
The benefits of cloud computing for scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency are well acknowledged. However,
deeper integration of cloud solutions into the capital markets infrastructure is required to unlock these benefits
fully. This involves not just adopting cloud technologies but also optimizing cloud-based platforms for data
analysis and investment strategy development across the market spectrum.
Cloud Computing for Scalability and Efficiency
Fintech collaborations have indeed played a crucial role in making financial products more accessible. Yet, to
truly democratize access to capital markets, there needs to be a concerted effort to expand these collaborations,
reaching underserved and rural populations. This requires innovative approaches and solutions that cater to the
unique needs of these segments, further simplifying investment processes and enhancing financial literacy.
Fintech Collaborations for Financial Inclusion
18
Despite the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) issuing guidelines to strengthen cybersecurity
practices, the constantly evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates ongoing vigilance and continuous
improvement of cybersecurity measures. Market participants and regulators must stay ahead of emerging
threats by adopting cutting-edge security technologies and practices.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Government Initiatives and Regulatory Environment
The regulatory framework and government initiatives in the Indian capital markets have evolved significantly to
promote transparency, efficiency, and investor protection. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI),
along with other regulatory bodies like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Insurance Regulatory and Development
Authority (IRDA), and Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), play pivotal roles in
overseeing various aspects of the financial sector. SEBI, in particular, regulates investment products and has
been instrumental in implementing policies to deepen the securities markets and foster innovations in financial
instruments.
A noteworthy regulatory aspect is the multiple regulatory architecture, which encompasses product-wise
regulators for different financial products, including credit, investment, insurance, and pension products. The
Forward Markets Commission (FMC), which was merged with SEBI in late 2015, exemplifies efforts to consolidate
regulatory oversight for enhanced market efficiency.
Quasi-regulatory agencies like the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), Small
Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), and National Housing Bank (NHB) also contribute to the regulatory
landscape by supervising and regulating specific financial institutions and activities. Central ministries,
especially the Ministry of Finance (MoF), and state governments through the Registrar of Cooperatives play a
significant role in policy-making and regulation.
The establishment of the Financial Sector Development Council (FSDC) marked an important development in
India's regulatory architecture. The FSDC, which replaced the High-Level Committee on Capital Markets, acts as
a council of regulators with the Finance Minister as chairman. It aims to resolve inter-agency disputes, oversee
the regulation of financial conglomerates, and perform wealth management functions dealing with multiple
products.
Recent developments by SEBI have focused on enhancing market activities and investor protection. For instance,
SEBI's amendments to the SEBI (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2021, and the introduction of a standard
operating procedure for the delisting of a listed subsidiary company through a scheme of arrangement highlight
the regulator's commitment to clarity and transparency in market operations. These amendments aim to
provide greater flexibility to issuers, ensure transparency in the issuance of non-convertible securities, and
clarify the criteria for companies in the same line of business seeking delisting.
Key initiatives include the implementation of more detailed disclosure requirements for market participants. This
move is designed to empower investors with crucial information necessary for making informed decisions, thus
strengthening investor protection and enhancing risk assessment. By requiring comprehensive disclosures
about risks specific to businesses, operations, and financial positions, SEBI aims to equip investors with the tools
needed for thorough risk assessments. This initiative not only improves corporate governance by mandating
transparency in related-party transactions, board composition, and remuneration policies but also ensures
market integrity by preventing the dissemination of false or misleading data. Moreover, these disclosure norms
CHAPTER 3
19

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
contribute to efficient price discovery, attracting both domestic and foreign investments and fostering market
development and innovation.
These regulatory advancements are a testament to SEBI's dedication to refining the operational efficiency of the
Indian Capital Markets ensuring they remain robust, transparent and investor-friendly amidst the evolving
global economic landscape.
The EY IPO Trends Report places Indian stock exchanges at the forefront of the global IPO arena in 2023
showcasing India's leadership in terms of the number of IPOs and its commendable 8th place ranking in terms of
funds raised. A diverse array of IPO activities has been noted in the mainboard including noteworthy fundraising
efforts by an infrastructure investment trust. Additionally the SME sector has demonstrated significant growth
signalling a buoyant trend in India's IPO activities. Key sectors leading this surge include Hospitality &
Construction, Automotive & Transportation, Diversified Industrial Products, and Real Estate, reflecting a broad-
based interest across various industries.
These positive movements are indicative of the concerted efforts by Indian Capital Markets to refine and
strengthen regulatory mechanisms, bolster corporate governance standards and enhance investor knowledge
and engagement. SEBI's regulatory updates aim to heighten market transparency and operational practices.
Innovations such as adjustments in issue pricing, the introduction of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for clearer
disclosures and the pioneering establishment of the Social Stock Exchange mark significant strides towards this
goal.
To address the evolving landscape of the Indian capital markets, the regulators needs to undertake several
targeted actions, particularly in the areas of sustainability, technological innovation, and financial literacy.
We need to harness AI and machine learning technologies to enhance its regulatory oversight capabilities.
Utilizing these technologies for real-time market surveillance can help in detecting unusual market activities
more efficiently, thereby preventing fraud and ensuring market integrity.
Implementing AI and Machine Learning in Regulatory Processes
The adoption of blockchain technology in the settlement and clearing process is another area the regulator
needs to explore. Blockchain can offer an immutable record of transactions, significantly reducing the risk of
fraud and errors, and streamlining the entire process for greater efficiency.
Leveraging Blockchain for Increased Transparency
20
While focusing on ESG reporting for larger corporations, SEBI also needs to develop specific ESG guidelines
tailored for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). These guidelines should recognize the unique
challenges and resource constraints faced by MSMEs, providing them with a feasible roadmap for sustainable
business practices that can enhance their attractiveness to socially conscious investors.
Developing a Comprehensive ESG Framework for MSMEs

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Given the burgeoning interest in cryptocurrency and digital assets, India needs to introduce regulatory
sandboxes specific to this domain. This would allow for the experimentation with crypto-related products in a
controlled environment, helping SEBI to formulate appropriate regulations that ensure investor protection while
fostering innovation.
Introducing Sandbox Regulations for Cryptocurrency
21
To boost financial literacy, SEBI may consider creating a unified digital platform offering curated educational
content tailored to different investor segments. This platform could leverage interactive tools, simulations, and
gamification to make learning about capital markets engaging and accessible to all, especially targeting
younger investors to cultivate a culture of informed investing from an early age.
Creating a Unified Digital Platform for Investor Education
The regulators needs to encourage the development and issuance of green bonds by offering regulatory
incentives and creating a supportive ecosystem. This would not only align with global sustainability goals but
also provide a boost to projects focused on renewable energy, waste management, and biodiversity
conservation within India.
Encouraging Development of Green Bonds

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Capital Markets for Indian SMEs
CHAPTER 4
SMEs have traditionally found it challenging to utilize traditional capital markets for financing largely due to an
ecosystem that has not been fully accommodating. Their unique financing needs especially for operational
liquidity and a scarcity of resources for managing regulatory compliance and navigating market intricacies
have been significant obstacles. Enhancing and simplifying the access mechanisms to make them both cost-
efficient and user-friendly is vital. Such improvements would significantly empower SMEs offering them an
effective pathway to harness capital markets for their funding requirements thereby fostering their growth and
development in a positive and formal manner.
SME IPOs
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
2022
2023
2024*
43
67
135
144
54
27
59
109
182
19
260.21
536.68
1,752.88
2,396.82
657
168
787
1,980
4,967
557
Year
No. of IPOs
Amount Raised
(in Rs. Crore)
3
Initially, the number of IPOs and the capital raised showed variability, with a notable increase peaking in 2018.
Following a downturn in 2019 and 2020, influenced by market volatility, there was a significant recovery, reaching
an all-time high in 2023 in terms of both the number of IPOs and the amount raised. The early data for 2024
suggests a decrease, indicating a potential normalization of market activities or the preliminary nature of the
year's data. This trend analysis reflects the increasing utilization and success of IPOs as a financing mechanism,
highlighting the growing confidence in the market.
22

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
BSE and the NSE have established specialized platforms for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) designated as
BSE SME and NSE EMERGE respectively. These platforms have been specifically designed to furnish SMEs with a
more accessible channel for securing capital via the public market. They permit listings under more lenient
criteria in comparison to those required for the main board, thus catering to the distinctive requirements of SMEs.
Though there is a noticeable shift towards these markets, a significant number of SMEs lack knowledge about the
listing requirements and procedures on stock exchanges. The costs associated with listing even on the Bombay
Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange remain prohibitive for many.
From the time of SME establishments the platforms BSE SME and NSE Emerge have witnessed a consistent rise in
SME listings. A substantial number of SMEs that have pursued listings on these platforms have experienced
notable growth following their public offering. This growth is evidenced by an increase in their stock prices, along
with enhanced visibility and credibility within the investor community.
In an effort to bolster SME participation in capital markets the Indian government along with regulatory entities
such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) have introduced a suite of initiatives and policies. These
include the simplification of compliance norms to lower the regulatory and compliance hurdles for SMEs aiming
to list on specialized SME platforms the establishment of a Fund of Funds by the Small Industries Development
Bank of India (SIDBI) to provide indirect financial support to SMEs thereby aiding their growth and ensuring they
meet the prerequisites for listing.
Despite these initiatives, SMEs in India face significant barriers to accessing capital markets. These challenges
stem from a lack of awareness and prevalent misconceptions about the complexity and cost of listing on SME
exchanges. Additionally the extensive preparation required for a public listing including financial restructuring
and meeting corporate governance standards can be overwhelming for SMEs. However, the considerable
benefits of accessing capital markets for Indian SMEs are evident. Entering public markets can supply the
essential capital needed for growth, enhance corporate governance, and boost visibility and credibility among
both customers and investors.
Key areas for the growth and development of SMEs
To stimulate growth in SME capital markets, it's essential to develop a robust investor base that is keen on
investing in SMEs. This involves not just attracting institutional investors but also individual investors who see
value in SME growth. Policy measures could include tax incentives for investments in SME sectors, creation of
dedicated SME investment funds, and facilitating platforms that connect SMEs with potential investors.
Encouraging venture capital and private equity investments into SMEs by providing regulatory ease and
financial incentives can also play a significant role.
Building Investor Bases for SME Markets
Market literacy is critical for both SMEs and investors. For SMEs, understanding the nuances of accessing capital
markets, the requirements for listing, and how to manage investor relations is crucial. For investors,
understanding the unique value proposition of SMEs, the risk profile, and the potential for growth within the SME
Enhancing Market Literacy Among SMEs and Investors
23

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Reducing the time it takes for SMEs to raise funds is vital for their growth and operational efficiency. Simplifying
regulatory requirements, creating fast-track listing processes for SMEs, and enabling technology-driven
platforms for quicker fundraising can significantly help. For example, digital crowdfunding platforms and peer-
to-peer lending can offer SMEs quicker access to capital. Regulatory sandbox environments can also be created
to test innovative financing models without the normal regulatory constraints
Speeding Up Fund-Raising for SMEs
Streamlining the listing process on stock exchanges for SMEs is crucial. This can involve reducing the paperwork,
lowering the costs associated with listing, and providing a simplified regulatory framework that balances
investor protection with the need for SMEs to access public markets. The development of dedicated SME trading
platforms or boards within existing exchanges can also provide tailored listing options that are more suited to the
needs and capabilities of SMEs.
Simplifying Listing Procedures
Transparency and the flow of information are fundamental to a thriving SME capital market. Regularly publishing
data on SME performance, market trends, and investment opportunities can boost investor confidence and SME
visibility. Creating online portals and databases where such information is readily accessible will help in making
informed decisions for both SMEs and investors.
Ensuring Effective Information Dissemination
24
sector are essential. Workshops, seminars, and digital platforms offering resources and training can significantly
enhance market literacy. Regulatory bodies and industry associations could collaborate to create educational
content and certification programs for SMEs and investors.
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
A Comparative Analysis
CHAPTER 5
Recent data reveals that India has reached an unprecedented peak in its share of global market capitalization,
around 3.4%, which surpasses its long-term average of 2.5%. This achievement places India at the forefront of
global market valuation contributors, highlighting its growing influence and resilience in the face of a general
decline in global market capitalization.
With China's economic growth rate decelerating, there is a marked shift towards India as an alternative
epicentre for growth, cementing its role as a critical driver in both emerging and global markets. Furthermore the
combination of possessing the largest general and youthful populations globally which presents a
demographic advantage along with a government that is both market-friendly and democratically elected
provides a solid basis for stock selection and the potential for outstanding performance.
Comparatively, when looking at the Indian and US stock markets, there are notable differences in performance,
volatility, sector dominance, and valuations. Over the past ten years, the Dow Jones Index has generally offered
better returns than the BSE Sensex, with a more stable performance. The correlation between the two markets
suggests a semi-strong relationship, indicating the importance of cautious diversification strategies. Indian
markets have been riskier, with higher volatility compared to the US markets. In terms of sector weightage,
financials dominate the Indian indices, whereas tech firms have more weight in the US markets. Valuation-wise,
the Sensex has a higher PE ratio, suggesting market expectations of faster earnings growth for Indian companies
compared to US companies.
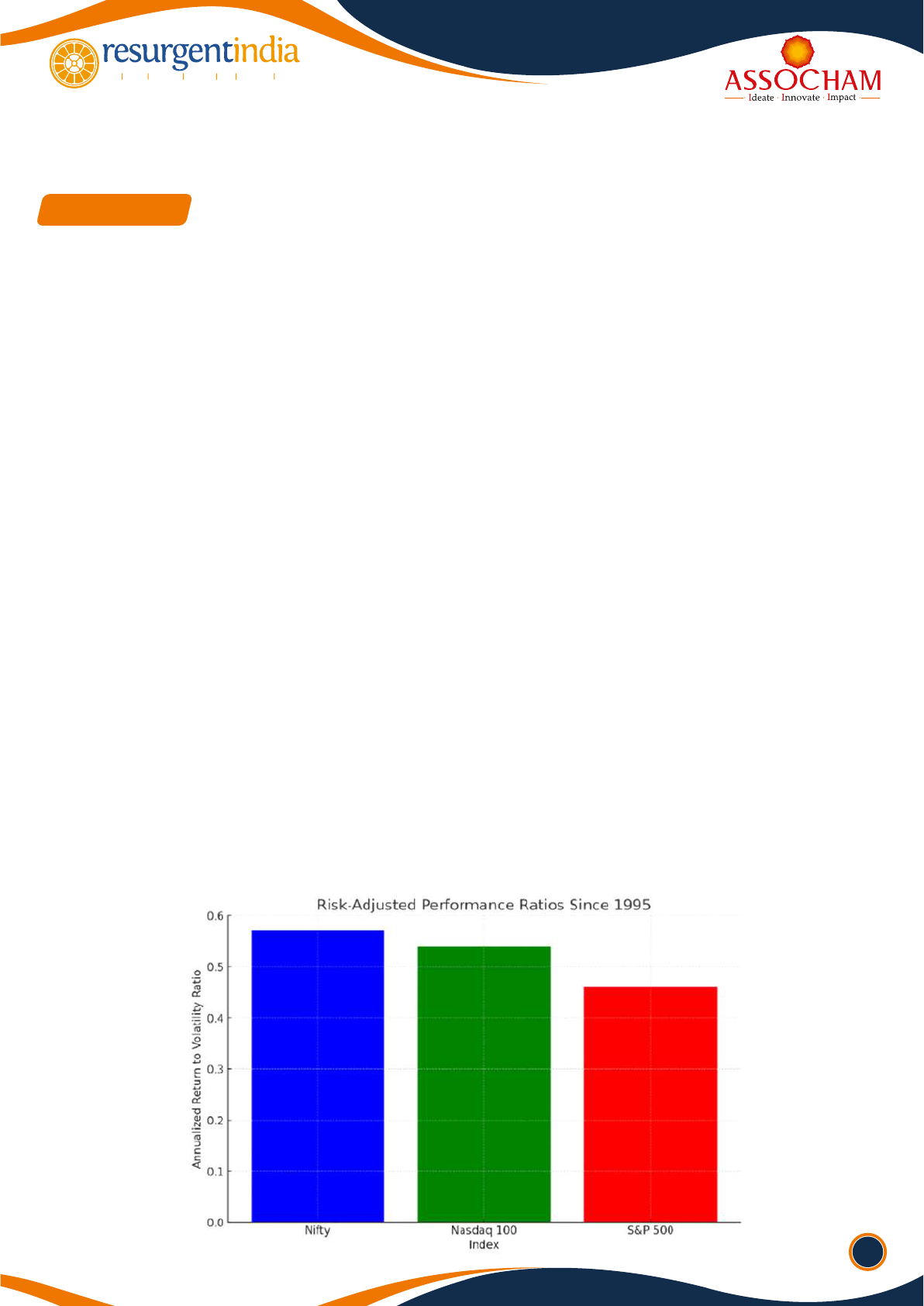
Since its inception in 1995, the Nifty, India's benchmark equity index, has demonstrated a notable annualized
return to volatility ratio of 0.57. This outperforms the ratios of the Nasdaq 100 (0.54) and the S&P 500 (0.46),
indicating that the Indian market has historically provided strong returns for lower volatility.
25

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
The bar chart above illustrates the Risk-Adjusted Performance Ratios since 1995 for the Nifty, Nasdaq 100, and S&P
500 indices. It highlights that the Nifty has outperformed both the Nasdaq 100 and S&P 500 in terms of the
annualized return to volatility ratio, showcasing the Indian market's capacity to provide strong returns with lower
volatility historically.
The bar chart above conceptually illustrates the comparison of market size and activity, highlighting the market
capitalization of the Indian stock market in relation to the combined markets of Korea and Taiwan, as well as
trading volumes in comparison to Hong Kong. India's significant position in the global financial landscape is
conspicuous, with its market capitalization surpassing that of Korea and Taiwan combined, and a thriving capital
market evinced by the number of IPOs exceeding those issued by the United States.
India is set to join the JPMorgan Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) on June 28, 2024, with a
potential weight of up to 10%. This inclusion is expected to enhance the bond market's depth, diminish risk
premiums, lower capital costs, and fortify debt sustainability.
Furthermore, the low correlation of Indian equities with global markets, as highlighted by the MSCI India Index's
beta of approximately 0.6 to the MSCI Emerging Markets Index, underscores India's improved economic.
Additionally, India's recognition as a low geopolitical risk nation within the emerging market spectrum, along with
its status as an oil importer, positions it to potentially benefit from stable or decreasing oil.
26

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Key Findings
CHAPTER 6
India's capital markets have undergone a transformative journey over the past two decades, emerging as a
formidable force on the global financial stage. With market capitalization reaching an impressive $4.379 trillion
by December 2023, India now ranks among the top five highest-valued countries worldwide, a testament to its
burgeoning financial sector and the increasing confidence of both domestic and international investors. This
growth trajectory has been significantly bolstered by the advent of digital trading platforms and a progressive
regulatory landscape, aimed at enhancing market transparency and stability. However, challenges such as
India's exclusion from major global government bond debt indexes highlight the need for strategic interventions
to harness its economic size and market potential fully.
Against this backdrop, India's Vision 2047 articulates an ambitious blueprint for transforming the nation into a
developed economy, emphasizing the pivotal role of capital markets in mobilizing resources for infrastructure,
technological innovation, and economic growth. The following points outline strategic recommendations to
navigate the complexities of an evolving financial ecosystem.
1. Market Cap and Global Influence: India's impressive market capitalization not only showcases its
economic strength but also its potential to shape global finance. To capitalize on this, India could spearhead
international finance forums and alliances, advocating for more inclusive global finance policies and creating
bilateral investment treaties to ease cross-border investments.
2. Capital Formation and Infrastructure: Directing savings into national development through
infrastructure bonds offers a dual benefit: ensuring robust returns for investors and funding critical projects. India
could incentivize these bonds through tax benefits and guarantees, making them a cornerstone for funding
ambitious infrastructure projects aligned with smart city initiatives and rural development.
3. Sector-Specific Funds for Vision 2047: To materially support Vision 2047, India could focus on creating
27

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
sector specific funds. These funds, supported by both government and private sector expertise, would not only
provide capital but also mentorship, fostering innovation that aligns with India's developmental goals.
4. Attracting Foreign Investment: Beyond easing regulatory barriers, India could implement a
comprehensive strategy for global outreach, involving diplomatic engagement, investment roadshows, and
targeted marketing campaigns highlighting its robust legal and economic reforms. Establishing India-centric
investment funds in key foreign markets could also act as a conduit for funneling investments into Indian
enterprises.
5. Financing Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Introducing innovation-focused investment vehicles could
channelize funds into high-growth sectors. Additionally, tax incentives for corporate investments in innovation
hubs would encourage more private sector involvement in nurturing entrepreneurship.
6. Promoting Green Finance: Introducing a green bond market framework that includes standardized
metrics for environmental impact and benefits could help in the promotion of green finance.
7. Technology-Driven Financial Inclusion: Leveraging India's strong IT sector to develop user-friendly
platforms for underserved populations could accelerate financial inclusion, integrating more citizens into the
financial growth narrative. Partnering with fintech companies to develop localized financial education apps
would ensure that the benefits of financial inclusion are widely understood and embraced.
8. Diversifying the IPO Market: To encourage a broader range of companies to go public, India could begin
with simplifying the IPO process for tech and green energy firms and introduce fast-track approval lanes. This,
combined with public awareness campaigns highlighting the benefits of investing in these sectors, could help
diversify investment options.
9. Corporate Debt Market: The establishment of a partial credit guarantee fund could de-risk investments
in corporate bonds, particularly for infrastructure projects. This would make corporate bonds more attractive to
pension funds and insurance companies, diversifying their investment portfolios.
10. Enhancing SME Access to Capital Markets: Simplifying the listing process on SME platforms and reducing
associated costs could encourage more SMEs to access public markets. Launching a nationwide mentorship
program that pairs upcoming SMEs with experienced market players could demystify the process of going
public, enhancing SME participation in capital markets.
These suggestions aim to harness the current strengths of India's capital markets while addressing areas for
growth and innovation, laying a foundation for sustained economic development aligned with India's strategic
goals.
28

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Report Sources:
• Unlocking India’s Capital Markets Potential _ S&P Global.pdf
• https://mospi.gov.in/105-capital-markets
• https://nasscom.in/knowledge-center/publications/technology-sector-india-2023-
strategic-review
• https://www2.deloitte.com/in/en/pages/technology/articles/tech-trends-2023.html
• https://investorsarchive.ltimindtree.com/insights/resources/tech-trends-global-capital-
markets-fy-2023
• https://www.globalxetfs.com/india-outlook-2024-the-secular-growth-story/
• https://www.spglobal.com/en/research-insights/featured/special-editorial/look-
forward/unlocking-india-s-capital-markets-potential
• https://www.businesstoday.in/markets/stocks/story/india-share-global-market-
capitalisation-all-time-high-what-lies-ahead-346625-2022-09-07
29

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training
Disclaimer
The information contained in the document is of a general nature and is not intended
to address the objectives, financial situations, or needs of any particular individual or
entity. It is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, nor should
it be regarded in any manner whatsoever, as advice and is not intended to influence a
person in making a decision, including, if applicable, in relation to a financial product or
an interest in a financial product. Although we endeavor to provide accurate and
timely information, there can be no guarantee that such information is accurate or
that it will continue to be accurate in the future. No one should act on such information
without appropriate professional advice and without a thorough examination of the
particular situation.

Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training

About ASSOCHAM
The Associated Chambers of Commerce & Industry of India (ASSOCHAM) is the country’s oldest apex chamber. It
brings in actionable insights to strengthen the Indian ecosystem, leveraging its network of more than 4,50,000
members, of which MSMEs represent a large segment. With a strong presence in states, and key cities globally,
ASSOCHAM also has more than 400 associations, federations, and regional chambers in its fold.
Aligned with the vision of creating a New India, ASSOCHAM works as a conduit between the industry and the
Government. The Chamber is an agile and forward-looking institution, leading various initiatives to enhance the
global competitiveness of the Indian industry, while strengthening the domestic ecosystem.
With more than 100 national and regional sector councils, ASSOCHAM is an impactful representative of the Indian
industry. These Councils are led by well-known industry leaders, academicians, economists and independent
professionals. The Chamber focuses on aligning critical needs and interests of the industry with the growth
aspirations of the nation.
ASSOCHAM is driving four strategic priorities – Sustainability, Empowerment, Entrepreneurship and Digitisation.
The Chamber believes that affirmative action in these areas would help drive an inclusive and sustainable
socio-economic growth for the country.
ASSOCHAM is working hand in hand with the government, regulators, and national and international think tanks
to contribute to the policy making process and share vital feedback on implementation of decisions of far-
reaching consequences. In line with its focus on being future-ready, the Chamber is building a strong network of
knowledge architects. Thus, ASSOCHAM is all set to redefine the dynamics of growth and development in the
technology-driven ‘Knowledge-Based Economy. The Chamber aims to empower stakeholders in the Indian
economy by inculcating knowledge that will be the catalyst of growth in the dynamic global environment.
The Chamber also supports civil society through citizenship programmes, to drive inclusive development.
ASSOCHAM’s member network leads initiatives in various segments such as empowerment, healthcare,
education and skilling, hygiene, affirmative action, road safety, livelihood, life skills, sustainability, to name a few.
The Knowledge Architect of Corporate India

RESURGENT INDIA LTD.
SEBI - Registered CAT - I Merchant Bank
Regn. No. INM000012144 / ISO 9001 : 2015 Certified
Mob. : +91 7840 000 667
www.resurgentindia.com
PAN INDIA PRESENCE
AHMEDABAD
MUMBAI
PUNE
GURGAON
LUDHIANA
JAIPUR
UDAIPUR
SURAT
BANGALORE
LUCKNOW
VARANASI
KOLKATA
BHOPAL
INDORE
BHUBANESWAR
HYDERABAD
CHENNAI
LEADING INVESTMENT BANKING FIRM
LEADING INVESTMENT BANKING FIRMLEADING INVESTMENT BANKING FIRM
TEV STUDY & DPR
VALUATION & TRANSACTION
ADVISORY
RESTRUCTURING
DEBT SYNDICATION
EQUITY FUNDRAISING
MERGERS & ACQUISITIONS
LEGAL SERVICES
ASM / LIE REPORT
SERVICES OFFERING
Debt
Equity
Valuaon
Advisory
TEV
Insolvency
Training

The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India
4th Floor, YMCA Cultural Centre and Library Building,
01, Jai Singh Road, New Delhi - 110001
Tel : 011-46550500 (Hunting Line) Fax: 011-23017008, 23017009
www.assocham.org
