
201-103-RE - Calculus 1
WORKSHEET: LIMITS
1. Use the graph of the function f(x) to answer each question.
Use ∞, −∞ or DNE where appropriate.
(a) f(0) =
(b) f(2) =
(c) f(3) =
(d) lim
x→0
−
f(x) =
(e) lim
x→0
f(x) =
(f) lim
x→3
+
f(x) =
(g) lim
x→3
f(x) =
(h) lim
x→−∞
f(x) =
2. Use the graph of the function f(x) to answer each question.
Use ∞, −∞ or DNE where appropriate.
(a) f(0) =
(b) f(2) =
(c) f(3) =
(d) lim
x→−1
f(x) =
(e) lim
x→0
f(x) =
(f) lim
x→2
+
f(x) =
(g) lim
x→∞
f(x) =

3. Evaluate each limit using algebraic techniques.
Use ∞, −∞ or DNE where appropriate.
(a) lim
x→0
x
2
− 25
x
2
− 4x − 5
(b) lim
x→5
x
2
− 25
x
2
− 4x − 5
(c) lim
x→1
7x
2
− 4x − 3
3x
2
− 4x + 1
(d) lim
x→−2
x
4
+ 5x
3
+ 6x
2
x
2
(x + 1) − 4(x + 1)
(e) lim
x→−3
|x + 1| +
3
x
(f) lim
x→3
√
x + 1 − 2
x
2
− 9
(g) lim
x→3
√
x
2
+ 7 − 3
x + 3
(h) lim
x→2
x
2
+ 2x − 8
√
x
2
+ 5 − (x + 1)
(i) lim
y→5
2y
2
+ 2y + 4
6y − 3
1/3
(j) lim
x→0
4
p
2 cos(x) − 5
(k) lim
x→0
1
3 + x
−
1
3 − x
x
(l) lim
x→−6
2x + 8
x
2
− 12
−
1
x
x + 6
(m) lim
x→∞
√
x
2
− 2 −
√
x
2
+ 1
(n) lim
x→−∞
√
x − 2 −
√
x
(o) lim
x→7
6
√
2x − 14
(p) lim
x→1
−
√
3 − 3x
(q) lim
x→∞
x
4
− 10
4x
3
+ x
(r) lim
x→−∞
3
r
x − 3
5 − x
(s) lim
x→∞
3x
3
+ x
2
− 2
x
2
+ x − 2x
3
+ 1
(t) lim
x→∞
x + 5
2x
2
+ 1
(u) lim
x→−∞
cos
x
5
+ 1
x
6
+ x
5
+ 100
(v) lim
x→2
2x
x
2
− 4
(w) lim
x→−1
3x
x
2
+ 2x + 1
(x) lim
x→−1
x
2
− 25
x
2
− 4x − 5
(y) lim
x→3
√
x
2
− 5 + 2
x − 3
(z) lim
x→0
2
x
+ sin(x)
x
4
(A) lim
x→1
−
1
x − 1
+ e
x
2
(B) lim
x→∞
2x
2
− 3x
(C) lim
x→0
√
x + 2 −
√
2 − x
x
(D) lim
x→0
+
e
x
1 + ln(x)
(E) lim
x→∞
√
x
2
+ 1 − 2x
(F) lim
x→1
3
√
x − 1
√
x − 1

4. Find the following limits involving absolute values.
(a) lim
x→1
x
2
− 1
|x − 1|
(b) lim
x→−2
1
|x + 2|
+ x
2
(c) lim
x→3
−
x
2
|x − 3|
x − 3
5. Find the value of the parameter k to make the following limit exist and be finite.
What is then the value of the limit?
lim
x→5
x
2
+ kx − 20
x − 5
6. Answer the following questions for the piecewise defined function f (x) described on
the right hand side.
(a) f(1) =
(b) lim
x→0
f(x) =
(c) lim
x→1
f(x) =
f(x) =
(
sin(πx) for x < 1,
2
x
2
for x > 1.
7. Answer the following questions for the piecewise defined function f(t) described on
the right hand side.
(a) f(−3/2) =
(b) f(2) =
(c) f(3/2) =
(d) lim
t→−2
f(t) =
(e) lim
t→−1
+
f(t) =
(f) lim
t→2
f(t) =
(g) lim
t→0
f(t) =
f(t) =
t
2
for t < −2
t + 6
t
2
− t
for − 1 < t < 2
3t − 2 for t ≥ 2

ANSWERS:
1. (a) DNE (b) 0 (c) 3 (d) −∞ (e) DNE (f) 2 (g) DNE (h) 1
2. (a) 0 (b) DNE (c) 0 (d) DNE (e) 0 (f) −∞ (g) 1
3.
(a) 5
(b)
5
3
(c) 5
(d) 1
(e) 1
(f)
1
24
(g)
1
6
(h) −18
(i)
4
3
(j) DNE
(k) −
2
9
(l)
1
36
(m) 0
(n) DNE
(o) DNE
(p) 0
(q) ∞
(r) −1
(s) −
3
2
(t) 0
(u) 1
(v) DNE
(w) −∞
(x) DNE
(y) DNE
(z) ∞
(A) −∞
(B) ∞
(C)
1
√
2
(D) 0
(E) −∞
(F)
2
3
4. (a) DNE (b) ∞ (c) −9
5. k = −1, limit is then equal to 9
6. (a) DNE (b) 0 (c) DNE
7. (a) DNE (b) 4 (c) 10 (d) DNE (e)
5
2
(f) 4 (g) DNE
8. (a) 0 (b) 0 (c)
5
3

Name
Pre-Calculus Rational functions worksheet
For each of the rational functions find: a. domain b. holes c. vertical asymptotes d. horizontal
asymptotes e. y-intercept f. x-intercepts
1.
2
2
2
6
xx
fx
xx
2.
2
2
2
1
x
fx
x
3.
3
2
fx
x
4.
21x
fx
x
5.
2
2
12
9
xx
fx
x
6.
2
4
3
x
fx
x

7.
2
1
xx
fx
x
8.
2
2
1
xx
fx
x
9.
2
1
32
x
fx
xx
10.
2
2
9
23
x
fx
xx

201-103-RE - Calculus 1
WORKSHEET: CONTINUITY
1. For each graph, determine where the function is discontinuous. Justify for each
point by: (i) saying which condition fails in the definition of continuity, and (ii) by
mentioning which type of discontinuity it is.
(a)
(b)
2. For each function, determine the interval(s) of continuity.
(a) f(x) = x
2
+ e
x
(b) f(x) =
3x + 1
2x
2
− 3x − 2
(c) f(x) =
4
√
5 − x
(d)* f(x) =
2
4 − x
2
+
1
√
x
2
− x − 12
3. For each piecewise defined function, determine where f(x) is continuous (or where it
is discontinuous). Justify your answer in detail.
(a) f(x) =
2
x
− 3x
2
for x ≤ 1
log
10
(x) + x for x > 1
(b) f(x) =
2x
3−x
for x ≤ 0
x
2
− 3x for 0 < x < 2
x
2
−8
x
for x > 2
4. Find all the value(s) of the parameter c (if possible), to make the given function
continuous everywhere.
(a) f(x) =
(
c · 3
x
− x
2
+ 2c for x ≤ 0
2x
5
+ c(x + 1) + 16 for x > 0

(b) f(x) =
(
2(cx)
3
+ x − 1 for x ≤ 1
2cx + (x − 1)
2
for x > 1
(c) f(x) =
3x + c for x < −1
x
2
− c for − 1 ≤ x ≤ 2
3 for x > 2
5.* Consider the function f(x) = bxc, the greatest integer function (also called the floor
function or the step function). Where is this function discontinuous?
6.* Find an example of a function such that the limit exists at every x, but that has
an infinite number of discontinuities. (You can describe the function and/or write a
formula down and/or draw a graph.)
PARTIAL ANSWERS:
1. (a) x = 0, 3 (b) x = −2, 0, 1
2. (a) R (b) R\{−1/2, 2} (c) (−∞, 5] (d) (−3, 2) ∪ (−2, 2) ∪ (2, 4)
3. (a) discontinuous only at x = 1 (b) discontinuous only at x = 2
4. (a) c = 8 (b) c = −1, 0, 1 (c) no solution possible
5. discontinuous at every integer, x = . . . , −3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3, . . .
6. many answers are possible, show me your solution!

201-103-RE - Calculus 1
WORKSHEET: DEFINITION OF THE DERIVATIVE
1. For each function given below, calculate the derivative at a point f
0
(a)
using the limit definition.
(a) f(x) = 2x
2
− 3x f
0
(0) =?
(b) f (x) =
√
2x + 1 f
0
(4) =?
(c) f(x) =
1
x − 2
f
0
(3) =?
2. For each function f (x) given below, find the general derivative f
0
(x)
as a new function by using the limit definition.
(a) f(x) =
√
x − 4 f
0
(x) =?
(b) f (x) = −x
3
f
0
(x) =?
(c) f(x) =
x
x + 1
f
0
(x) =?
(d) f (x) =
1
√
x
f
0
(x) =?
3. For each function f (x) given below, find the equation of the tangent line
at the indicated point.
(a) f(x) = x − x
2
at (2, −2)
(b) f (x) = 1 − 3x
2
at (0, 1)
(c) f(x) =
1
2x
at x = 1
(d) f (x) = x +
√
x at x = 1
ANSWERS:
1. (a) f
0
(0) = −3 (b) f
0
(4) = 1/3 (c) f
0
(3) = −1
2. (a) f
0
(x) =
1
2
√
x−4
(b) f
0
(x) = −3x
2
(c) f
0
(x) =
1
(x+1)
2
(d) f
0
(x) =
−1
2x
3/2
3. (a) y = −3x + 4 (b) y = 1 (c) y = −
1
2
x + 1 (d) y =
3
2
x +
1
2

Derivative Practice Worksheet Name: ___________________________
Solve the derivatives for using basic differentiation.
1. y = 3
2.
2
4g x x
3.
2
2 3 6h t t t
4.
3
24s t t t
5.
23
1
2
4
xx
fx
x
6.
5yx
7.
4
3
7
2
1
35g x x x
x
8.
2
1
2
f x x x
9.
3
2
5yx
10.
2
1
3g x x
x
11.
3
1
3
hx
x
12.
x
y
x
13.
34
32f x x x x

14.
32
23
x
y
x
15.
2
2
32
1
xx
fx
x
16.
23
2 1 1g x x x x
17.
22
3 2 5y x x x
18.
2
52
1
x
fx
x
19.
9
4
yx
20.
1x
fx
x
21.
9
4
y
x
22.
23
4 3 3 2y x x x
23.
2
2
32
xx
y
x
24.
2
21
3
xx
y
x

Worksheet # 12: Higher Derivatives and Trigonometric Functions
1. Calculate the indicated derivative:
(a) f
(4)
(1), f(x) = x
4
(b) g
(3)
(5), g(x) = 2x
2
− x + 4
(c) h
(3)
(t), h(t) = 4e
t
− t
3
(d) s
(2)
(w), s(w) =
√
we
w
2. Calculate the first three derivatives of f(x) = xe
x
and use these to guess a general formula for f
(n)
(x),
the n-th derivative of f.
3. Let f (t) = t + 2 cos(t).
(a) Find all values of t where the tangent line to f at the point (t, f (t)) is horizontal.
(b) What are the largest and smallest values for the slope of a tangent line to the graph of f?
4. Differentiate each of the following functions:
(a) f(t) = cos(t)
(b) g(u) =
1
cos(u)
(c) r(θ) = θ
3
sin(θ)
(d) s(t) = tan(t) + csc(t)
(e) h(x) = sin(x) csc(x)
(f) f(x) = x
2
sin(x)
(g) g(x) = sec(x) + cot(x)
5. Calculate the first five derivatives of f(x) = sin(x). Then determine f
(8)
and f
(37)
6. Calculate the first 5 derivatives of f(x) = 1/x. Can you guess a formula for the nth derivative, f
(n)
?
7. A particle’s distance from the origin (in meters) along the x-axis is modeled by p(t) = 2 sin(t) − cos(t),
where t is measured in seconds.
(a) Determine the particle’s speed (speed is defined as the absolute value of velocity) at π seconds.
(b) Is the particle moving towards or away from the origin at π seconds? Explain.
(c) Now, find the velocity of the particle at time t =
3π
2
. Is the particle moving toward the origin or
away from the origin?
(d) Is the particle speeding up at
π
2
seconds?
8. Find an equation of the tangent line at the point specified:
(a) y = x
3
+ cos(x), x = 0
(b) y = csc(x) − cot(x), x =
π
4
(c) y = e
θ
sec(θ), θ =
π
4
9. Comprehension check for derivatives of trigonometric functions:
(a) True or False: If f
0
(θ) = − sin(θ), then f(θ) = cos(θ).
(b) True or False: If θ is one of the non-right angles in a right triangle and sin(θ) =
2
3
, then the
hypotenuse of the triangle must have length 3.

Math Excel Supplemental Problems #12
1. Use the Product Rule twice to find a formula for (fg)
00
in terms of f and g as well as their first and second
derivatives.
2. Calculate the first and second derivatives of the following functions:
(a) f (x) = x sin x
(b) f (x) =
e
x
cos x
(c) f (x) =
csc x
x
(d) f (x) = tan x
3. Calculate the first five derivatives of f(x) = cos x, then determine f
(8)
and f
(37)
©
C
N
2
S
0
c
1
h
3
j
d
K
J
u
n
t
v
a
P
z
S
7
o
I
f
k
t
d
w
e
a
N
r
d
e
R
n
L
Q
L
J
C
N
.
y
a
Z
A
0
l
u
l
n
M
r
l
i
t
g
Q
h
f
t
f
s
S
p
r
b
e
4
s
H
e
h
r
e
v
P
e
2
d
B
.
k
j
W
M
1
a
0
d
e
e
t
4
w
t
i
C
t
l
h
2
C
I
n
n
M
f
8
i
K
n
l
i
V
t
Z
e
r
q
C
n
a
K
l
s
c
D
u
K
l
G
u
r
s
L
.
e
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Calculus
©
s
9
2
B
0
T
1
F
3
4
Q
K
Z
u
u
t
4
a
8
R
S
C
o
h
f
g
t
z
w
b
a
o
r
F
e
A
C
L
t
L
h
C
Q
.
P
L
Y
A
0
l
h
l
A
2
r
J
i
J
g
H
h
B
t
9
s
q
P
r
9
e
G
s
z
e
c
r
q
v
R
e
v
d
e
.
2
Chain Rule Practice
Differentiate each function with respect to
x.
1)
y
(
x
)
2)
y
x
3)
f
(
x
)
(
x
)
x 4)
y
x
(
x
)
5)
y
(
x
)
(
x
)
6)
f
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
-1-

©
R
e
2
g
0
C
1
6
3
m
z
K
J
u
8
t
D
a
I
f
S
B
o
M
f
y
t
J
w
s
a
O
r
M
e
X
X
L
l
L
l
C
2
.
A
k
t
A
e
l
Q
l
6
q
r
Z
i
W
g
W
h
t
t
a
s
e
7
r
G
e
z
s
W
e
b
r
Y
v
g
e
h
d
d
.
m
Q
8
M
9
a
H
d
V
e
5
c
w
V
i
J
t
y
h
L
w
I
q
n
f
f
y
i
0
n
h
i
s
t
v
e
u
U
C
i
a
2
l
r
c
v
u
P
l
u
u
w
s
Z
.
N
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
7)
f
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
8)
f
(
x
)
x
x
9)
ysec
x
10)
f
(
x
)
(
x
)
csc
x
11)
f
(
x
)
cos
x
x
12)
f
(
x
)
sin
x
13)
f
(
x
)
x
tan
x
14)
ycot
x
-2-

©
T
M
2
G
0
j
1
f
3
F
X
K
T
u
v
t
3
a
n
i
S
p
o
Q
f
2
t
9
w
O
a
R
r
t
e
m
H
L
N
L
4
C
F
.
y
c
C
A
9
l
5
l
W
u
r
Y
i
m
g
h
h
1
t
T
s
y
m
r
6
e
O
s
5
e
V
r
3
v
k
e
j
d
W
.
I
d
2
M
v
a
t
d
t
e
I
N
w
5
i
n
t
k
h
Z
o
I
5
n
1
f
F
i
v
n
N
i
V
t
v
e
v
4
C
3
a
t
l
y
c
R
u
2
l
W
u
7
s
1
.
2
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-3-
Answers to Chain Rule Practice
1)
dy
dx
(
x
)
x
=
x
(
x
)
2)
dy
dx
(
x
)
x
=
x
(
x
)
3)
f
'
(
x
)
(
x
)
(
x
)
(
x
)
x
=
x
x
(
x
)
4)
dy
dx
(
x
)
(
x
)
(
x
)
x
=
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
5)
dy
dx
(
x
)
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
=
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
6)
f
'
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
=
x
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
7)
f
'
(
x
)
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
=
x
(
x
x
)
(
x
)
(
x
)
8)
f
'
(
x
)
(
x
)
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
(
x
)
=
x
x
(
x
)
(
x
)
9)
dy
dx
sec
x
tan
x
x
=
x
sec
x
tan
x
10)
f
'
(
x
)
(
x
)
csc
x
cot
x
x
csc
x
x
=
x
csc
x
(
x
cot
x
xcot
x
)

©
f
g
2
D
0
G
1
K
3
9
V
K
i
u
m
t
V
a
q
R
S
B
o
b
f
b
t
n
w
C
a
U
r
K
e
H
l
L
E
L
R
C
h
.
3
b
F
A
b
l
d
l
V
z
r
9
i
9
g
D
h
J
t
Z
s
2
H
r
E
e
K
s
j
e
M
r
t
v
m
e
X
d
L
.
f
f
F
M
d
a
r
d
v
e
k
m
w
9
i
e
t
E
h
V
R
I
D
n
y
f
9
i
W
n
f
i
0
t
T
e
T
r
C
1
a
L
l
q
c
P
u
V
l
q
u
I
s
O
.
K
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-4-
11)
f
'
(
x
)
cos
x
(
x
)
x
(
x
)
sin
x
x
=
x
(
x
sin
x
sin
x
xcos
x
)
(
x
)
12)
f
'
(
x
)
cos
x
x
=
x
cos
x
13)
f
'
(
x
)
tan
x
x
(
x
)
sec
x
x
tan
x
=
x
(
tan
x
x
sec
x
x
sec
x
)
tan
x
14)
dy
dx
csc
(
x
)
(
x
)
x
=
x
csc
(
x
)
(
x
)
Implicit differentiation worksheet for Calculus 1
Determine dy/dx for each of the following.
(1) y = x
2
+ xy
(2) x
2
y + y = 3
(3) x
1/4
+ y
1/4
= 2
(4) x
1/3
+ y
1/3
= 7
(5)
√
x +
√
y = 25
(6) x
2
+ y
2
= 1.1
(7) x
3
+ y
3
=
√
5
(8) x + sin(y) = y + 1
(9) y
√
x + x
√
y = 16
(10) x
2
+ xy − y
3
= xy
2
(11) x
2
+ y
2
=
√
7
(12) x
2/3
+ y
2/3
= a
2/3
(a is a constant)
(13) x
a
y
2
+ x
b
y + x
c
= 0 (a, b, c constants)
(14) sin(xy) = 2x + 5
(15) x ln(y) + y
3
= ln(x)
(16) e
cos(y)
= x
3
sin(y)
Determine d
2
y/dx
2
for each of the following.
(17) 1 − xy = x − y
2
(18) x − y = (x + y)
2
(19) x
2/3
+ y
2/3
= 8
(20) sin(x) − 4 cos(y) = y
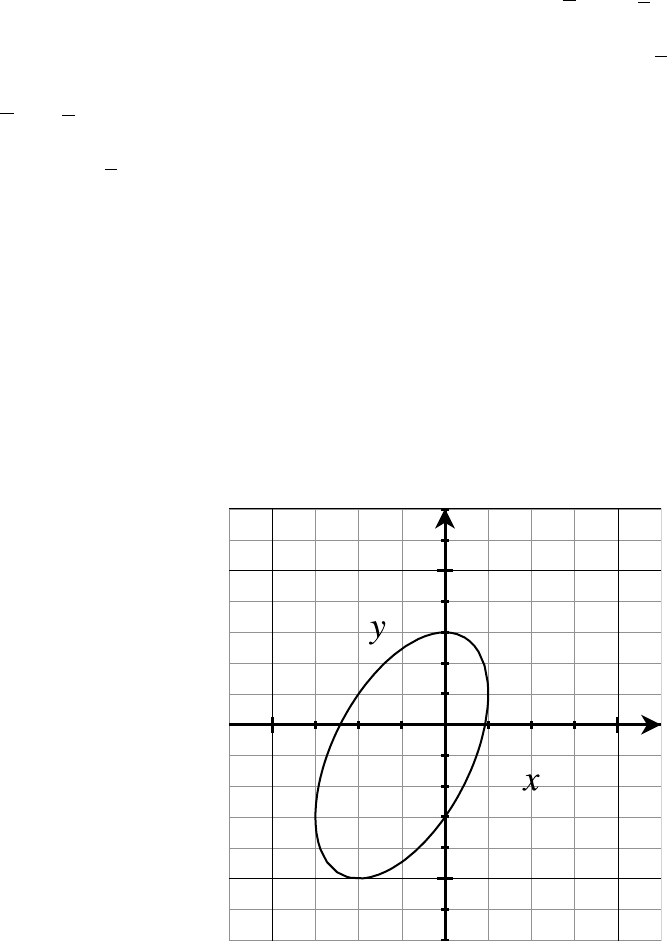
-8 0 8
-5
5
For the curve x
2
+ y
2
− xy + 3x − 9 = 0 (above),
(21) Determine dy/dx.
(22) Where do the horizontal tangent lines occur?
(23) Where do the vertical tangent lines occur (dy/dx = ±∞)?
(24) Determine d
2
y/dx
2
.

-4 -2 0 2 4
-4
-2
2
4
For the curve x
2
+ xy + y
2
= 5 (above),
(25) Determine dy/dx.
(26) Where do the horizontal tangent lines occur?
(27) Where do the vertical tangent lines occur (dy/dx = ±∞)?
(28) Determine d
2
y/dx
2
.
Consider the equation
(cos x)y
2
+ (3 sin x − 1)y + (7x − 2) = 0
(29) Check that x = 0, y = 2 satisfies this equation.
(30) Find dy/dx at the point (0, 2) using implicit differentiation.
(31) Use the quadratic formula to solve for y in terms of x. (Should you use “+” or “−”? Why?)
(32) Would you like to find dy/dx using that formula for y? (Me neither...)
Find f
0
(x) in terms of g(x) and g
0
(x), where g(x) > 0 for all x. (Hint: if a is a constant then g(a) is
constant.)
(33) f(x) = g(x)
3
(34) f(x) = g(x)(x − a)
(35) f(x) = g(a)(x − a)
(36) f(x) = g(x + g(x))
(37) f(x) =
g(x)
x − a
(38) f(x) =
1
g(x)
(39) f(x) = g(xg(a))
(40) f(x) =
p
g(x)
2
(41) f(x) =
p
g(x
2
)
(42) f(2x + 3) = g(x
2
)

©
6
h
2
v
0
a
1
0
2
Q
1
K
w
u
k
t
x
a
M
A
S
F
o
y
f
P
t
M
w
g
a
X
r
G
e
v
1
L
4
L
w
C
C
.
3
J
S
A
h
l
S
l
a
1
r
W
i
h
g
a
h
v
t
Q
s
8
I
r
x
e
f
s
E
e
0
r
f
v
v
e
d
d
g
.
i
w
u
M
q
a
D
d
c
e
r
E
w
h
i
C
t
x
h
z
M
I
8
n
t
f
G
i
w
n
I
i
c
t
I
e
c
Q
C
t
a
s
l
Y
c
S
u
N
l
L
u
f
s
q
.
4
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Logarithmic Differentiation
Use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate each function with respect to
x.
1)
y =
2
x
2
x
2)
y =
5
x
5
x
3)
y =
3
x
3
x
4)
y =
4
x
x
4
5)
y =
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
3
5
x
3
+ 1 6)
y =
(
x
5
+ 5
)
2
2
x
2
+ 3
7)
y =
(
3
x
4
− 2
)
5
(
3
x
3
+ 4
)
2
8)
y =
3
x
2
+ 1
(
3
x
4
+ 1
)
3
-1-

©
Z
X
2
w
0
3
1
9
2
4
d
K
4
u
S
t
9
a
G
V
S
t
o
5
f
G
t
L
w
r
a
E
r
b
e
f
X
L
E
L
F
C
B
.
u
3
N
A
H
l
L
l
a
m
r
C
i
9
g
F
h
N
t
Z
s
5
g
r
O
e
k
s
I
e
N
r
B
v
v
e
u
d
E
.
u
G
B
M
V
a
q
d
b
e
e
o
w
N
i
G
t
R
h
M
9
I
8
n
K
f
j
i
R
n
U
i
K
t
4
e
4
M
C
u
a
2
l
b
c
c
u
L
l
2
u
k
s
z
.
3
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
9)
y =
2
x
3
+ 3
(
x
4
− 3
)
3
10)
y =
(
2
x
2
− 5
)
3
x
2
− 2
Use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate each function with respect to
x. You do not need to
simplify or substitute for
y.
11)
y =
(
5
x − 4
)
4
(
3
x
2
+ 5
)
5
⋅
(
5
x
4
− 3
)
3
12)
y =
(
x + 2
)
4
⋅
(
2
x − 5
)
2
⋅
(
5
x + 1
)
3
13)
y =
(
5
x
5
+ 2
)
2
⋅
(
3
x
3
− 1
)
3
⋅
(
3
x − 1
)
4
14)
y =
(
x
2
+ 3
)
4
(
5
x
5
− 2
)
5
⋅
(
3
x
2
− 5
)
2
15)
y =
(
3
x
3
− 4
)
5
⋅
(
3
x − 1
)
3
⋅
(
5
x
3
− 2
)
2
⋅
(
x + 3
)
4
16)
y =
(
4
x
2
− 5
)
2
(
2
x − 3
)
4
⋅
(
5
x
4
− 2
)
5
⋅
(
3
x
2
− 4
)
3
-2-

©
Q
x
2
S
0
0
1
D
2
N
8
K
L
u
u
t
a
a
6
J
S
W
o
f
f
j
t
O
w
9
a
U
r
9
e
l
3
L
g
L
K
C
s
.
H
v
l
A
b
l
B
l
v
c
r
p
i
B
g
N
h
z
t
s
s
h
j
r
9
e
w
s
x
e
F
r
i
v
e
e
5
d
6
.
K
k
Z
M
W
a
7
d
C
e
g
w
w
E
i
W
t
6
h
n
z
I
c
n
m
f
w
i
q
n
8
i
g
t
F
e
b
q
C
a
a
J
l
E
c
S
u
C
l
E
u
o
s
b
.
u
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Logarithmic Differentiation
Use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate each function with respect to
x.
1)
y =
2
x
2
x
dy
dx
=
y
(
2 ln
x + 2
)
=
4
x
2
x
(
ln
x + 1
)
2)
y =
5
x
5
x
dy
dx
=
y
(
5 ln
x + 5
)
=
25
x
5
x
(
ln
x + 1
)
3)
y =
3
x
3
x
dy
dx
=
y
(
3 ln
x + 3
)
=
9
x
3
x
(
ln
x + 1
)
4)
y =
4
x
x
4
dy
dx
=
y
(
4
x
3
ln
x +
x
3
)
=
4
x
x
4
+ 3
(
4 ln
x + 1
)
5)
y =
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
3
5
x
3
+ 1
dy
dx
=
y
(
36
x
3
3
x
4
+ 4
+
15
x
2
10
x
3
+ 2
)
=
3
x
2
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
2
(
135
x
4
+ 24
x + 20
)
2
5
x
3
+ 1
6)
y =
(
x
5
+ 5
)
2
2
x
2
+ 3
dy
dx
=
y
(
10
x
4
x
5
+ 5
+
2
x
2
x
2
+ 3
)
=
2
x
(
x
5
+ 5
)(
11
x
5
+ 15
x
3
+ 5
)
2
x
2
+ 3
7)
y =
(
3
x
4
− 2
)
5
(
3
x
3
+ 4
)
2
dy
dx
=
y
(
60
x
3
3
x
4
− 2
−
18
x
2
3
x
3
+ 4
)
=
6
x
2
(
3
x
4
− 2
)
4
(
21
x
4
+ 40
x + 6
)
(
3
x
3
+ 4
)
3
8)
y =
3
x
2
+ 1
(
3
x
4
+ 1
)
3
dy
dx
=
y
(
3
x
3
x
2
+ 1
+
36
x
3
3
x
4
+ 1
)
=
3
x
(
3
x
4
+ 1
)
2
(
39
x
4
+ 1 + 12
x
2
)
3
x
2
+ 1
-1-

©
U
W
2
4
0
i
1
l
2
k
L
K
G
u
a
t
4
a
F
7
S
m
o
j
f
D
t
v
w
s
a
F
r
C
e
h
w
L
I
L
V
C
S
.
X
Y
u
A
Q
l
R
l
8
q
r
I
i
D
g
g
h
A
t
u
s
W
R
r
8
e
t
s
e
e
x
r
M
v
z
e
s
d
9
.
S
Z
B
M
H
a
7
d
A
e
a
o
w
5
i
I
t
D
h
j
m
I
Q
n
4
f
r
i
n
n
D
i
n
t
U
e
h
v
C
y
a
r
l
4
c
A
u
X
l
u
u
7
s
n
.
G
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
9)
y =
2
x
3
+ 3
(
x
4
− 3
)
3
dy
dx
=
y
(
3
x
2
2
x
3
+ 3
−
12
x
3
x
4
− 3
)
=
3
x
2
(
−7
x
4
− 3 − 12
x
)
(
x
4
− 3
)
4
2
x
3
+ 3
10)
y =
(
2
x
2
− 5
)
3
x
2
− 2
dy
dx
=
y
(
12
x
2
x
2
− 5
+
x
x
2
− 2
)
=
x
(
2
x
2
− 5
)
2
(
14
x
2
− 29
)
x
2
− 2
Use logarithmic differentiation to differentiate each function with respect to
x. You do not need to
simplify or substitute for
y.
11)
y =
(
5
x − 4
)
4
(
3
x
2
+ 5
)
5
⋅
(
5
x
4
− 3
)
3
dy
dx
=
y
(
20
5
x − 4
−
30
x
3
x
2
+ 5
−
60
x
3
5
x
4
− 3
)
12)
y =
(
x + 2
)
4
⋅
(
2
x − 5
)
2
⋅
(
5
x + 1
)
3
dy
dx
=
y
(
4
x + 2
+
4
2
x − 5
+
15
5
x + 1
)
13)
y =
(
5
x
5
+ 2
)
2
⋅
(
3
x
3
− 1
)
3
⋅
(
3
x − 1
)
4
dy
dx
=
y
(
50
x
4
5
x
5
+ 2
+
27
x
2
3
x
3
− 1
+
12
3
x − 1
)
14)
y =
(
x
2
+ 3
)
4
(
5
x
5
− 2
)
5
⋅
(
3
x
2
− 5
)
2
dy
dx
=
y
(
8
x
x
2
+ 3
−
125
x
4
5
x
5
− 2
−
12
x
3
x
2
− 5
)
15)
y =
(
3
x
3
− 4
)
5
⋅
(
3
x − 1
)
3
⋅
(
5
x
3
− 2
)
2
⋅
(
x + 3
)
4
dy
dx
=
y
(
45
x
2
3
x
3
− 4
+
9
3
x − 1
+
30
x
2
5
x
3
− 2
+
4
x + 3
)
16)
y =
(
4
x
2
− 5
)
2
(
2
x − 3
)
4
⋅
(
5
x
4
− 2
)
5
⋅
(
3
x
2
− 4
)
3
dy
dx
=
y
(
16
x
4
x
2
− 5
−
8
2
x − 3
−
100
x
3
5
x
4
− 2
−
18
x
3
x
2
− 4
)
-2-
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com

6.4 Exponential Growth and Decay Calculus
6.4 EXPONENTIAL GROWTH AND DECAY
In many applications, the rate of change of a variable y is proportional to the value of y. If y is a function of time t,
we can express this statement as
Example: Find the solution to this differential equation given the initial condition that when t = 0.
0
yy=
(This is the derivation of an exponential function … see notecards)
Exponential Growth and Decay Model
If y changes at a rate proportional to the amount present (
dy
dt
ky=
) and when t = 0, then
0
yy=
0
kt
yye=
where k is the proportional constant.
Exponential growth occurs when , and exponential decay occurs when .
0k > 0k <
Example: The rate of change of y is proportional to y. When t = 0, y = 2. When t = 2, y = 4. What is the value of y
when t = 3?
Example: [1985 AP Calculus BC #33] If
2
dy
dt
y
=−
and if y = 1 when t = 0, what is the value of t for which
1
2
y =
?
A)
1
2
ln 2−
B)
1
4
−
C)
1
2
ln 2
D)
2
2
E) ln 2
146

6.4 Exponential Growth and Decay Calculus
Example: Radioactive Decay: The rate at which a radioactive element decays (as measured
by the number of nuclei that change per unit of time) is approximately proportional to the
amount of nuclei present. Suppose that 10 grams of the plutonium isotope Pu-239 was
released in the Chernobyl nuclear accident. How long will it take for the 10 grams to decay t
1 gram? [Pu-239 has a half life of 24,360 years]
o
Example: Newton’s Law of Cooling: Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the
rate of change in the temperature of an object is proportional to the difference
between the object’s temperature and the temperature in the surrounding medium.
A detective finds a murder victim at 9 am. The temperature of the body is
measured at 90.3 °F. One hour later, the temperature of the body is 89.0 °F. The
temperature of the room has been maintained at a constant 68 °F.
(a) Assuming the temperature, T, of the body obeys Newton’s Law of
Cooling, write a differential equation for T.
(b) Solve the differential equation to estimate the time the murder occurred.
147

6.4 Exponential Growth and Decay Calculus
Example: [1988 AP Calculus BC #43] Bacteria in a certain culture increase at rate proportional to the number
present. If the number of bacteria doubles in three hours, in how many hours will the number of bacteria triple?
A)
3ln3
ln 2
B)
2ln3
ln 2
C)
ln3
ln 2
D)
27
ln
2
⎛⎞
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎝⎠
E)
9
ln
2
⎛⎞
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎝⎠
Example: [AP Calculus 1993 AB #42] A puppy weighs 2.0 pounds at birth and 3.5 pounds two months later. If the
weight of the puppy during its first 6 months is increasing at a rate proportional to its weight, then how much will
the puppy weigh when it is 3 months old?
A) 4.2 pounds B) 4.6 pounds C) 4.8 pounds D) 5.6 pounds E) 6.5 pounds
Example
: [1993 AP Calculus BC #38] During a certain epidemic, the number of people that are infected at any time
increases at rate proportional to the number of people that are infected at that time. If 1,000 people are infected
when the epidemic is first discovered, and 1,200 are infected 7 days later, how many people are infected 12 days
after the epidemic is first discovered?
A) 343 B) 1,343 C) 1,367 D) 1,400 E) 2,057
Example
: [1998 AP Calculus AB #84] Population y grows according to the equation
dy
dt
ky=
, where k is a constant
and
t is measured in years. If the population doubles every 10 years, then the value of k is
A) 0.069 B) 0.200 C) 0.301 D) 3.322 E) 5.000
Notecards from Section 6.4: Derivation of an exponential function
148
©
f
j
2
I
0
n
1
u
3
h
M
K
R
u
a
t
8
a
D
m
S
N
o
w
f
V
t
z
w
j
a
K
r
Q
e
6
t
L
s
L
z
C
t
.
F
H
f
A
D
l
P
l
u
9
r
w
i
E
g
H
h
n
t
z
s
L
i
r
i
e
m
s
3
e
o
r
Y
v
4
e
N
d
U
.
4
9
X
M
G
a
s
d
F
e
w
T
w
8
i
z
t
c
h
h
9
I
Y
n
X
f
r
i
7
n
M
i
V
t
v
e
S
V
C
x
a
i
l
i
c
6
u
H
l
Y
u
i
s
J
.
4
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Related Rates
Solve each related rate problem.
1) Water leaking onto a floor forms a circular pool. The radius of the pool increases at a rate of 4
cm/min. How fast is the area of the pool increasing when the radius is 5 cm?
2) Oil spilling from a ruptured tanker spreads in a circle on the surface of the ocean. The area of
the spill increases at a rate of 9
π m²/min. How fast is the radius of the spill increasing when the
radius is 10 m?
3) A conical paper cup is 10 cm tall with a radius of 10 cm. The cup is being filled with water so
that the water level rises at a rate of 2 cm/sec. At what rate is water being poured into the cup
when the water level is 8 cm?
-1-

©
q
M
2
y
0
b
1
z
3
9
f
K
T
u
q
t
6
a
I
l
S
L
o
E
f
1
t
o
w
6
a
9
r
i
e
Q
H
L
u
L
O
C
S
.
h
X
d
A
g
l
4
l
J
d
r
I
i
2
g
2
h
g
t
F
s
W
X
r
k
e
e
s
h
e
x
r
P
v
X
e
9
d
S
.
3
1
p
M
u
a
3
d
y
e
m
v
w
Q
i
2
t
B
h
J
T
I
R
n
0
f
p
i
7
n
X
i
c
t
O
e
j
B
C
r
a
u
l
D
c
o
u
v
l
k
u
P
s
p
.
B
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
4) A spherical balloon is inflated so that its radius (
r) increases at a rate of
2
r
cm/sec. How fast is
the volume of the balloon increasing when the radius is 4 cm?
5) A 7 ft tall person is walking away from a 20 ft tall lamppost at a rate of 5 ft/sec. Assume the
scenario can be modeled with right triangles. At what rate is the length of the person's shadow
changing when the person is 16 ft from the lamppost?
6) An observer stands 700 ft away from a launch pad to observe a rocket launch. The rocket
blasts off and maintains a velocity of 900 ft/sec. Assume the scenario can be modeled as a right
triangle. How fast is the observer to rocket distance changing when the rocket is 2400 ft from
the ground?
-2-

©
2
y
2
q
0
d
1
G
3
4
c
K
K
u
l
t
U
a
W
y
S
W
o
k
f
x
t
K
w
z
a
m
r
H
e
J
e
L
8
L
4
C
o
.
0
I
p
A
3
l
c
l
b
p
r
n
i
o
g
M
h
U
t
O
s
4
l
r
R
e
e
s
2
e
F
r
g
v
j
e
K
d
b
.
j
S
z
M
B
a
8
d
g
e
n
k
w
9
i
f
t
e
h
Q
A
I
P
n
J
f
R
i
g
n
U
i
Q
t
Q
e
s
P
C
o
a
p
l
3
c
O
u
6
l
3
u
k
s
S
.
4
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Related Rates
Solve each related rate problem.
1) Water leaking onto a floor forms a circular pool. The radius of the pool increases at a rate of 4
cm/min. How fast is the area of the pool increasing when the radius is 5 cm?
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dr
dt
= 4 Find:
dA
dt
r = 5
dA
dt
r = 5
=
2
πr ⋅
dr
dt
= 40
π cm²/min
2) Oil spilling from a ruptured tanker spreads in a circle on the surface of the ocean. The area of
the spill increases at a rate of 9
π m²/min. How fast is the radius of the spill increasing when the
radius is 10 m?
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dA
dt
= 9
π Find:
dr
dt
r = 10
dr
dt
r = 10
=
1
2
πr
⋅
dA
dt
=
9
20
m/min
3) A conical paper cup is 10 cm tall with a radius of 10 cm. The cup is being filled with water so
that the water level rises at a rate of 2 cm/sec. At what rate is water being poured into the cup
when the water level is 8 cm?
V = volume of material in cone
h = height
t = time
Equation:
V =
πh
3
3
Given rate:
dh
dt
= 2 Find:
dV
dt
h = 8
dV
dt
h = 8
=
πh
2
⋅
dh
dt
= 128
π cm³/sec
-1-

©
f
7
2
F
0
g
1
f
3
z
X
K
5
u
n
t
P
a
A
x
S
7
o
k
f
y
t
N
w
O
a
7
r
K
e
h
u
L
h
L
i
C
8
.
i
M
G
A
I
l
e
l
f
e
r
f
i
H
g
T
h
X
t
G
s
1
5
r
L
e
3
s
l
e
4
r
9
v
Q
e
i
d
j
.
m
6
y
M
8
a
6
d
L
e
l
f
w
6
i
b
t
6
h
v
D
I
A
n
b
f
g
i
I
n
T
i
k
t
v
e
N
l
C
m
a
p
l
y
c
j
u
P
l
O
u
i
s
H
.
w
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
4) A spherical balloon is inflated so that its radius (
r) increases at a rate of
2
r
cm/sec. How fast is
the volume of the balloon increasing when the radius is 4 cm?
V = volume of sphere
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
V =
4
3
π
r
3
Given rate:
dr
dt
=
2
r
Find:
dV
dt
r = 4
dV
dt
r = 4
=
4
π
r
2
⋅
dr
dt
= 32
π cm³/sec
5) A 7 ft tall person is walking away from a 20 ft tall lamppost at a rate of 5 ft/sec. Assume the
scenario can be modeled with right triangles. At what rate is the length of the person's shadow
changing when the person is 16 ft from the lamppost?
x = distance from person to lamppost
y = length of shadow
t = time
Equation:
x +
y
20
=
y
7
Given rate:
dx
dt
= 5 Find:
dy
dt
x = 16
dy
dt
x = 16
=
7
13
⋅
dx
dt
=
35
13
ft/sec
6) An observer stands 700 ft away from a launch pad to observe a rocket launch. The rocket
blasts off and maintains a velocity of 900 ft/sec. Assume the scenario can be modeled as a right
triangle. How fast is the observer to rocket distance changing when the rocket is 2400 ft from
the ground?
a = altitute of rocket
z = distance from observer to rocket
t = time
Equation:
a
2
+ 490000 =
z
2
Given rate:
da
dt
= 900 Find:
dz
dt
a = 2400
dz
dt
a = 2400
=
a
z
⋅
da
dt
= 864 ft/sec
-2-
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com

©
g
5
2
P
0
l
1
3
3
e
5
K
t
u
3
t
l
a
Y
t
S
W
o
B
f
R
t
c
w
S
a
w
r
k
e
Q
m
L
z
L
z
C
D
.
u
2
7
A
k
l
G
l
f
l
r
b
i
E
g
k
h
j
t
b
s
A
9
r
l
e
w
s
S
e
I
r
2
v
P
e
V
d
W
.
L
2
7
M
z
a
5
d
W
e
I
g
w
b
i
M
t
M
h
N
b
I
m
n
F
f
0
i
E
n
E
i
s
t
U
e
t
S
C
D
a
l
l
J
c
r
u
1
l
s
u
T
s
G
.
k
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
©
8
b
2
3
0
5
1
9
3
o
l
K
0
u
C
t
5
a
i
F
S
H
o
p
f
i
t
c
w
k
a
d
r
9
e
e
M
L
B
L
1
C
v
.
0
h
c
A
5
l
r
l
x
8
r
z
i
8
g
T
h
z
t
Z
s
9
2
r
J
e
j
s
q
e
p
r
T
v
C
e
V
d
y
.
w
4.6 Related Rates
Solve each related rate problem.
1) A spherical balloon is deflated so that its radius decreases at a rate of 4 cm/sec. At what rate is
the volume of the balloon changing when the radius is 3 cm?
2) A spherical balloon is deflated at a rate of
256
π
3
cm³/sec. At what rate is the radius of the
balloon changing when the radius is 8 cm?
3) Water leaking onto a floor forms a circular pool. The radius of the pool increases at a rate of 9
cm/min. How fast is the area of the pool increasing when the radius is 12 cm?
4) A 7 ft tall person is walking towards a 17 ft tall lamppost at a rate of 4 ft/sec. Assume the
scenario can be modeled with right triangles. At what rate is the length of the person's shadow
changing when the person is 12 ft from the lamppost?
5) A conical paper cup is 30 cm tall with a radius of 10 cm. The cup is being filled with water at a
rate of
2
π
3
cm³/sec. How fast is the water level rising when the water level is 2 cm?
6) A 13 ft ladder is leaning against a wall and sliding towards the floor. The top of the ladder is
sliding down the wall at a rate of 7 ft/sec. How fast is the base of the ladder sliding away from
the wall when the base of the ladder is 12 ft from the wall?
7) Oil spilling from a ruptured tanker spreads in a circle on the surface of the ocean. The radius of
the spill increases at a rate of 2 m/min. How fast is the area of the spill increasing when the
radius is 13 m?
8) A hypothetical cube shrinks so that the length of its sides are decreasing at a rate of 2 m/min.
At what rate is the volume of the cube changing when the sides are 2 m each?
9) A conical paper cup is 10 cm tall with a radius of 10 cm. The bottom of the cup is punctured
so that the water level goes down at a rate of 2 cm/sec. At what rate is the volume of water in
the cup changing when the water level is 9 cm?
10) An observer stands 500 ft away from a launch pad to observe a rocket launch. The rocket
blasts off and maintains a velocity of 700 ft/sec. Assume the scenario can be modeled as a right
triangle. How fast is the observer to rocket distance changing when the rocket is 1200 ft from
the ground?
11) A spherical snowball melts at a rate of 36
π in³/sec. At what rate is the radius of the snowball
changing when the radius is 5 in?
-1-

©
d
w
2
E
0
W
1
n
3
n
x
K
P
u
8
t
5
a
e
J
S
u
o
2
f
q
t
o
w
z
a
9
r
S
e
K
p
L
4
L
i
C
V
.
P
O
2
A
9
l
Z
l
6
i
r
6
i
d
g
H
h
O
t
D
s
7
b
r
0
e
e
s
W
e
P
r
v
v
O
e
Y
d
F
.
1
O
W
M
a
a
i
d
G
e
H
P
w
T
i
m
t
M
h
7
Z
I
4
n
W
f
n
i
N
n
c
i
O
t
I
e
I
M
C
v
a
7
l
J
c
J
u
u
l
e
u
M
s
9
.
A
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
12) A hypothetical cube grows at a rate of 8 m³/min. How fast are the sides of the cube increasing
when the sides are 2 m each?
13) A conical paper cup is 10 cm tall with a radius of 30 cm. The cup is being filled with water so
that the water level rises at a rate of 2 cm/sec. At what rate is water being poured into the cup
when the water level is 9 cm?
14) Water slowly evaporates from a circular shaped puddle. The radius of the puddle decreases at
a rate of 8 in/hr. Assuming the puddle retains its circular shape, at what rate is the area of the
puddle changing when the radius is 3 in?
15) A hypothetical square grows so that the length of its diagonals are increasing at a rate of 4
m/min. How fast is the area of the square increasing when the diagonals are 14 m each?
16) Water slowly evaporates from a circular shaped puddle. The area of the puddle decreases at a
rate of 16
π in²/hr. Assuming the puddle retains its circular shape, at what rate is the radius of
the puddle changing when the radius is 12 in?
17) A hypothetical cube grows so that the length of its sides are increasing at a rate of 4 m/min.
How fast is the volume of the cube increasing when the sides are 7 m each?
18) A hypothetical square grows at a rate of 16 m²/min. How fast are the sides of the square
increasing when the sides are 15 m each?
19) A hypothetical cube shrinks at a rate of 8 m³/min. At what rate are the sides of the cube
changing when the sides are 3 m each?
20) A spherical snowball melts so that its radius decreases at a rate of 4 in/sec. At what rate is the
volume of the snowball changing when the radius is 8 in?
21) A perfect cube shaped ice cube melts so that the length of its sides are decreasing at a rate of 2
mm/sec. Assume that the block retains its cube shape as it melts. At what rate is the volume of
the ice cube changing when the sides are 2 mm each?
22) A conical paper cup is 10 cm tall with a radius of 10 cm. The bottom of the cup is punctured
so that the water leaks out at a rate of
9
π
4
cm³/sec. At what rate is the water level changing
when the water level is 6 cm?
23) A hypothetical square shrinks so that the length of its diagonals are changing at a rate of
−8
m/min. At what rate is the area of the square changing when the diagonals are 5 m each?
24) A hypothetical square shrinks at a rate of 2 m²/min. At what rate are the diagonals of the
square changing when the diagonals are 7 m each?
25) Water leaking onto a floor forms a circular pool. The area of the pool increases at a rate of
25
π cm²/min. How fast is the radius of the pool increasing when the radius is 6 cm?
-2-

©
e
b
2
o
0
K
1
s
3
3
R
K
6
u
r
t
t
a
G
x
S
v
o
1
f
y
t
q
w
W
a
E
r
E
e
8
d
L
A
L
i
C
p
.
J
P
0
A
o
l
1
l
n
j
r
g
i
b
g
J
h
h
t
e
s
Y
L
r
C
e
E
s
o
e
d
r
A
v
u
e
j
d
z
.
m
h
s
M
q
a
o
d
W
e
z
T
w
W
i
x
t
v
h
q
R
I
l
n
K
f
n
i
g
n
G
i
r
t
W
e
f
a
C
3
a
F
l
d
c
J
u
c
l
a
u
Y
s
C
.
K
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-3-
Answers to 4.6 Related Rates
1)
V = volume of sphere
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
V =
4
3
π
r
3
Given rate:
dr
dt
=
−4 Find:
dV
dt
r = 3
dV
dt
r = 3
=
4
πr
2
⋅
dr
dt
= −144
π cm³/sec
2)
V = volume of sphere
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
V =
4
3
π
r
3
Given rate:
dV
dt
=
−
256
π
3
Find:
dr
dt
r = 8
dr
dt
r = 8
=
1
4
πr
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
−
1
3
cm/sec
3)
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dr
dt
= 9 Find:
dA
dt
r = 12
dA
dt
r = 12
=
2
πr ⋅
dr
dt
= 216
π cm²/min
4)
x = distance from person to lamppost
y = length of shadow
t = time
Equation:
x +
y
17
=
y
7
Given rate:
dx
dt
=
−4 Find:
dy
dt
x = 12
dy
dt
x = 12
=
7
10
⋅
dx
dt
=
−
14
5
ft/sec
5)
V = volume of material in cone
h = height
t = time
Equation:
V =
πh
3
27
Given rate:
dV
dt
=
2
π
3
Find:
dh
dt
h = 2
dh
dt
h = 2
=
9
πh
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
3
2
cm/sec
6)
x = horizontal distance from base of ladder to wall
y = vertical distance from top of ladder to floor
t = time
Equation:
x
2
+
y
2
=
13
2
Given rate:
dy
dt
=
−7 Find:
dx
dt
x = 12
dx
dt
x = 12
=
−
y
x
⋅
dy
dt
=
91
12
ft/sec
7)
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dr
dt
= 2 Find:
dA
dt
r = 13
dA
dt
r = 13
=
2
πr ⋅
dr
dt
= 52
π m²/min

©
j
C
2
8
0
a
1
C
3
3
x
K
s
u
K
t
Y
a
q
X
S
4
o
e
f
9
t
G
w
2
a
P
r
V
e
Y
4
L
J
L
q
C
c
.
N
h
0
A
p
l
m
l
Q
1
r
c
i
z
g
p
h
t
t
L
s
G
P
r
n
e
O
s
1
e
r
r
W
v
7
e
M
d
J
.
8
p
M
M
O
a
T
d
h
e
h
L
w
p
i
K
t
j
h
n
0
I
w
n
N
f
m
i
j
n
R
i
W
t
c
e
4
0
C
3
a
9
l
S
c
i
u
K
l
l
u
h
s
4
.
x
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-4-
8)
V = volume of cube
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
V =
s
3
Given rate:
ds
dt
=
−2 Find:
dV
dt
s = 2
dV
dt
s = 2
=
3
s
2
⋅
ds
dt
= −24 m³/min
9)
V = volume of material in cone
h = height
t = time
Equation:
V =
πh
3
3
Given rate:
dh
dt
=
−2 Find:
dV
dt
h = 9
dV
dt
h = 9
=
πh
2
⋅
dh
dt
= −162
π cm³/sec
10)
a = altitute of rocket
z = distance from observer to rocket
t = time
Equation:
a
2
+ 250000 =
z
2
Given rate:
da
dt
= 700 Find:
dz
dt
a = 1200
dz
dt
a = 1200
=
a
z
⋅
da
dt
=
8400
13
ft/sec
11)
V = volume of sphere
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
V =
4
3
π
r
3
Given rate:
dV
dt
=
−36
π Find:
dr
dt
r = 5
dr
dt
r = 5
=
1
4
πr
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
−
9
25
in/s
12)
V = volume of cube
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
V =
s
3
Given rate:
dV
dt
= 8 Find:
ds
dt
s = 2
ds
dt
s = 2
=
1
3
s
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
2
3
m/min
13)
V = volume of material in cone
h = height
t = time
Equation:
V = 3
πh
3
Given rate:
dh
dt
= 2 Find:
dV
dt
h = 9
dV
dt
h = 9
=
9
πh
2
⋅
dh
dt
= 1458
π cm³/sec
14)
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dr
dt
=
−8 Find:
dA
dt
r = 3
dA
dt
r = 3
=
2
πr ⋅
dr
dt
= −48
π in²/hr

©
A
f
2
e
0
j
1
O
3
f
m
K
e
u
6
t
E
a
h
a
S
T
o
7
f
9
t
q
w
R
a
J
r
c
e
b
h
L
y
L
C
C
4
.
w
8
T
A
G
l
y
l
W
m
r
K
i
9
g
w
h
e
t
s
s
n
z
r
G
e
0
s
w
e
L
r
6
v
p
e
b
d
1
.
Q
8
J
M
5
a
p
d
e
e
o
T
w
o
i
5
t
6
h
L
P
I
i
n
i
f
g
i
A
n
g
i
W
t
1
e
g
k
C
p
a
H
l
k
c
9
u
3
l
q
u
Q
s
S
.
p
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-5-
15)
A = area of square
x = length of diagonals
t = time
Equation:
A =
x
2
2
Given rate:
dx
dt
= 4 Find:
dA
dt
x = 14
dA
dt
x = 14
=
x ⋅
dx
dt
= 56 m²/min
16)
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dA
dt
=
−16
π Find:
dr
dt
r = 12
dr
dt
r = 12
=
1
2
πr
⋅
dA
dt
=
−
2
3
in/hr
17)
V = volume of cube
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
V =
s
3
Given rate:
ds
dt
= 4 Find:
dV
dt
s = 7
dV
dt
s = 7
=
3
s
2
⋅
ds
dt
= 588 m³/min
18)
A = area of square
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
A =
s
2
Given rate:
dA
dt
= 16 Find:
ds
dt
s = 15
ds
dt
s = 15
=
1
2
s
⋅
dA
dt
=
8
15
m/min
19)
V = volume of cube
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
V =
s
3
Given rate:
dV
dt
=
−8 Find:
ds
dt
s = 3
ds
dt
s = 3
=
1
3
s
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
−
8
27
m/min
20)
V = volume of sphere
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
V =
4
3
π
r
3
Given rate:
dr
dt
=
−4 Find:
dV
dt
r = 8
dV
dt
r = 8
=
4
πr
2
⋅
dr
dt
= −1024
π in³/sec
21)
V = volume of cube
s = length of sides
t = time
Equation:
V =
s
3
Given rate:
ds
dt
=
−2 Find:
dV
dt
s = 2
dV
dt
s = 2
=
3
s
2
⋅
ds
dt
= −24 mm³/sec

©
c
H
2
L
0
z
1
e
3
1
i
K
9
u
k
t
B
a
R
d
S
Y
o
z
f
J
t
L
w
X
a
P
r
V
e
C
p
L
r
L
D
C
e
.
Q
h
G
A
N
l
R
l
S
A
r
H
i
0
g
P
h
C
t
7
s
E
J
r
e
e
4
s
1
e
z
r
6
v
L
e
2
d
n
.
m
X
1
M
H
a
v
d
t
e
s
b
w
p
i
z
t
w
h
E
2
I
y
n
U
f
P
i
e
n
w
i
6
t
Q
e
Y
e
C
R
a
A
l
C
c
2
u
S
l
3
u
u
s
o
.
n
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
-6-
22)
V = volume of material in cone
h = height
t = time
Equation:
V =
πh
3
3
Given rate:
dV
dt
=
−
9
π
4
Find:
dh
dt
h = 6
dh
dt
h = 6
=
1
πh
2
⋅
dV
dt
=
−
1
16
cm/sec
23)
A = area of square
x = length of diagonals
t = time
Equation:
A =
x
2
2
Given rate:
dx
dt
=
−8 Find:
dA
dt
x = 5
dA
dt
x = 5
=
x ⋅
dx
dt
= −40 m²/min
24)
A = area of square
x = length of diagonals
t = time
Equation:
A =
x
2
2
Given rate:
dA
dt
=
−2 Find:
dx
dt
x = 7
dx
dt
x = 7
=
1
x
⋅
dA
dt
=
−
2
7
m/min
25)
A = area of circle
r = radius
t = time
Equation:
A =
π
r
2
Given rate:
dA
dt
= 25
π Find:
dr
dt
r = 6
dr
dt
r = 6
=
1
2
πr
⋅
dA
dt
=
25
12
cm/min

©
H
8
2
A
0
o
1
m
3
x
Q
K
m
u
I
t
N
a
C
F
S
m
o
e
f
D
t
E
w
Z
a
7
r
V
e
J
X
L
Q
L
N
C
a
.
M
1
3
A
k
l
P
l
A
G
r
d
i
P
g
d
h
D
t
f
s
2
k
r
L
e
o
s
5
e
W
r
J
v
G
e
D
d
i
.
M
S
p
M
d
a
H
d
Y
e
a
0
w
B
i
e
t
m
h
H
A
I
2
n
Z
f
W
i
W
n
s
i
Y
t
v
e
y
o
C
o
a
A
l
L
c
q
u
c
l
G
u
t
s
z
.
q
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Assignment
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima.
1)
y =
x
3
− 5
x
2
+ 7
x − 5
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima. You may use the provided graph to
sketch the function.
2)
y =
x
3
− 6
x
2
+ 9
x + 1
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
-1-

©
g
b
2
S
0
i
1
g
3
s
Q
K
i
u
r
t
5
a
C
X
S
i
o
B
f
I
t
i
w
X
a
4
r
K
e
e
r
L
C
L
M
C
b
.
C
C
d
A
S
l
L
l
d
S
r
l
i
2
g
j
h
P
t
k
s
V
k
r
y
e
o
s
b
e
x
r
2
v
G
e
0
d
C
.
l
N
4
M
P
a
k
d
Q
e
p
n
w
P
i
D
t
m
h
e
j
I
A
n
Q
f
b
i
A
n
p
i
6
t
g
e
a
R
C
e
a
M
l
j
c
m
u
1
l
T
u
R
s
p
.
U
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima.
3)
y =
−
x
3
− 3
x
2
− 1 4)
y =
x
4
− 2
x
2
+ 3
5)
y =
x
4
−
x
2
6)
y =
−
2
x
2
− 4
7)
y =
(
2
x − 8
)
2
3
8)
y =
−
1
5
(
x − 4
)
5
3
−
2
(
x − 4
)
2
3
Critical thinking questions:
9) Give an example function
f
(
x
)
where
f
''
(
0
)
= 0 and there is no relative minimum or maximum at
x = 0.
10) Give an example function
f
(
x
)
where
f
''
(
0
)
= 0 and there is a relative maximum at
x = 0.
-2-

©
u
u
2
1
0
R
1
4
3
j
h
K
E
u
H
t
4
a
s
n
S
w
o
1
f
2
t
V
w
l
a
g
r
7
e
E
E
L
y
L
V
C
E
.
B
S
E
A
j
l
4
l
k
F
r
u
i
o
g
G
h
U
t
5
s
f
s
r
G
e
i
s
i
e
Z
r
h
v
P
e
Z
d
p
.
9
r
6
M
t
a
n
d
s
e
I
t
w
k
i
0
t
r
h
Y
8
I
8
n
b
f
R
i
I
n
D
i
o
t
w
e
S
A
C
S
a
U
l
p
c
n
u
H
l
z
u
H
s
B
.
K
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Assignment
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima.
1)
y =
x
3
− 5
x
2
+ 7
x − 5
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Relative minimum:
(
7
3
,
−
86
27
)
Relative maximum:
(
1, −2
)
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima. You may use the provided graph to
sketch the function.
2)
y =
x
3
− 6
x
2
+ 9
x + 1
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Relative minimum:
(
3, 1
)
Relative maximum:
(
1, 5
)
-1-

©
R
u
2
f
0
8
1
i
3
7
u
K
g
u
8
t
2
a
1
e
S
o
o
7
f
4
t
m
w
G
a
1
r
5
e
i
4
L
k
L
n
C
x
.
Y
y
j
A
h
l
n
l
g
a
r
X
i
U
g
n
h
u
t
r
s
i
H
r
j
e
F
s
Z
e
F
r
i
v
g
e
p
d
m
.
v
h
i
M
J
a
v
d
N
e
p
z
w
6
i
U
t
N
h
o
q
I
K
n
U
f
Z
i
9
n
o
i
v
t
l
e
h
m
C
C
a
o
l
D
c
T
u
Q
l
9
u
n
s
8
.
l
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
For each problem, find all points of relative minima and maxima.
3)
y =
−
x
3
− 3
x
2
− 1
Relative minimum:
(
−2, −5
)
Relative maximum:
(
0, −1
)
4)
y =
x
4
− 2
x
2
+ 3
Relative minima:
(
−1, 2
)
,
(
1, 2
)
Relative maximum:
(
0, 3
)
5)
y =
x
4
−
x
2
Relative minima:
(
−
2
2
,
−
1
4
)
,
(
2
2
,
−
1
4
)
Relative maximum:
(
0, 0
)
6)
y =
−
2
x
2
− 4
Relative minimum:
(
0,
1
2
)
No relative maxima.
7)
y =
(
2
x − 8
)
2
3
Relative minimum:
(
4, 0
)
No relative maxima.
8)
y =
−
1
5
(
x − 4
)
5
3
−
2
(
x − 4
)
2
3
Relative minimum:
(
0,
−
12
3
2
5
)
Relative maximum:
(
4, 0
)
Critical thinking questions:
9) Give an example function
f
(
x
)
where
f
''
(
0
)
= 0 and there is no relative minimum or maximum at
x = 0.
Many answers. Ex:
f
(
x
)
= 0,
x,
x
3
, etc
10) Give an example function
f
(
x
)
where
f
''
(
0
)
= 0 and there is a relative maximum at
x = 0.
Many answers. Ex:
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
4
-2-
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com

©
a
6
2
C
0
z
1
b
3
e
D
K
G
u
S
t
w
a
S
r
S
9
o
d
f
6
t
V
w
V
a
H
r
V
e
f
7
L
B
L
h
C
U
.
q
l
I
A
D
l
Y
l
9
r
r
B
i
x
g
2
h
x
t
m
s
a
7
r
U
e
J
s
H
e
g
r
3
v
X
e
Z
d
5
.
8
Q
h
M
v
a
8
d
R
e
4
h
w
b
i
C
t
y
h
P
N
I
3
n
n
f
0
i
U
n
Y
i
X
t
C
e
I
t
C
f
a
E
l
5
c
s
u
b
l
k
u
t
s
H
.
S
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Absolute Extrema
For each problem, find all points of absolute minima and maxima on the given closed interval.
1)
y =
−
x
3
− 6
x
2
− 9
x + 3; [−3, −1]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
2)
y =
8
x
2
+ 4
; [0, 5]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
3)
y =
x
3
+ 6
x
2
+ 9
x + 3; [−4, 0] 4)
y =
x
4
− 3
x
2
+ 4; [−1, 1]
5)
y =
x
2
3
x − 6
; [3, 6]
6)
y =
(
x + 2
)
2
3
; [−4, −2]
-1-

©
E
P
2
z
0
5
1
g
3
y
0
K
g
u
F
t
B
a
g
m
S
4
o
C
f
H
t
E
w
I
a
s
r
Q
e
w
x
L
M
L
H
C
y
.
T
E
z
A
P
l
M
l
w
F
r
s
i
H
g
V
h
P
t
m
s
6
Y
r
v
e
m
s
T
e
N
r
d
v
u
e
k
d
v
.
O
9
P
M
q
a
O
d
C
e
o
F
w
p
i
N
t
1
h
F
z
I
l
n
6
f
S
i
Q
n
i
i
F
t
l
e
A
h
C
1
a
u
l
I
c
Y
u
e
l
B
u
2
s
e
.
N
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
For each problem, find all points of absolute minima and maxima on the given interval.
7)
y =
x
3
− 3
x
2
− 3; (0, 3)
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
8)
y =
(
5
x + 25
)
1
3
; [−2, 2]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
9)
y =
x
3
− 3
x
2
+ 6; [0,
∞) 10)
y =
x
4
− 2
x
2
− 3; (0,
∞)
11)
y =
4
x
2
+ 2
; (−5, −2]
12)
y =
−
1
6
(
x + 1
)
7
3
+
14
3
(
x + 1
)
1
3
; (−5, 0)
-2-

©
y
F
2
G
0
B
1
g
3
K
j
K
A
u
D
t
p
a
y
S
S
e
o
G
f
G
t
a
w
5
a
M
r
p
e
4
3
L
z
L
L
C
V
.
0
W
J
A
4
l
X
l
8
D
r
v
i
I
g
3
h
t
t
U
s
W
g
r
l
e
u
s
f
e
3
r
S
v
V
e
y
d
T
.
r
e
u
M
2
a
h
d
8
e
4
i
w
V
i
6
t
j
h
6
A
I
W
n
O
f
C
i
U
n
U
i
h
t
N
e
e
M
C
3
a
K
l
G
c
Q
u
X
l
g
u
f
s
N
.
W
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Absolute Extrema
For each problem, find all points of absolute minima and maxima on the given closed interval.
1)
y =
−
x
3
− 6
x
2
− 9
x + 3; [−3, −1]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Absolute minimum:
(
−3, 3
)
Absolute maximum:
(
−1, 7
)
2)
y =
8
x
2
+ 4
; [0, 5]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Absolute minimum:
(
5,
8
29
)
Absolute maximum:
(
0, 2
)
3)
y =
x
3
+ 6
x
2
+ 9
x + 3; [−4, 0]
Absolute minima:
(
−4, −1
)
,
(
−1, −1
)
Absolute maxima:
(
0, 3
)
,
(
−3, 3
)
4)
y =
x
4
− 3
x
2
+ 4; [−1, 1]
Absolute minima:
(
−1, 2
)
,
(
1, 2
)
Absolute maximum:
(
0, 4
)
5)
y =
x
2
3
x − 6
; [3, 6]
Absolute minimum:
(
4,
8
3
)
Absolute maxima:
(
3, 3
)
,
(
6, 3
)
6)
y =
(
x + 2
)
2
3
; [−4, −2]
Absolute minimum:
(
−2, 0
)
Absolute maximum:
(
−4,
3
4
)
-1-

©
t
W
2
r
0
j
1
G
3
l
G
K
2
u
3
t
5
a
e
W
S
1
o
z
f
z
t
h
w
T
a
0
r
T
e
j
c
L
9
L
Q
C
L
.
m
Z
f
A
Z
l
S
l
D
I
r
L
i
X
g
e
h
P
t
w
s
h
s
r
b
e
D
s
P
e
J
r
U
v
R
e
E
d
5
.
J
0
D
M
v
a
C
d
f
e
B
M
w
q
i
M
t
v
h
9
L
I
q
n
k
f
t
i
6
n
q
i
E
t
2
e
N
u
C
W
a
Y
l
L
c
8
u
Y
l
C
u
4
s
K
.
Q
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
For each problem, find all points of absolute minima and maxima on the given interval.
7)
y =
x
3
− 3
x
2
− 3; (0, 3)
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Absolute minimum:
(
2, −7
)
No absolute maxima.
8)
y =
(
5
x + 25
)
1
3
; [−2, 2]
x
y
−8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8
−8
−6
−4
−2
2
4
6
8
Absolute minimum:
(
−2,
3
15
)
Absolute maximum:
(
2,
3
35
)
9)
y =
x
3
− 3
x
2
+ 6; [0,
∞)
Absolute minimum:
(
2, 2
)
No absolute maxima.
10)
y =
x
4
− 2
x
2
− 3; (0,
∞)
Absolute minimum:
(
1, −4
)
No absolute maxima.
11)
y =
4
x
2
+ 2
; (−5, −2]
No absolute minima.
Absolute maximum:
(
−2,
2
3
)
12)
y =
−
1
6
(
x + 1
)
7
3
+
14
3
(
x + 1
)
1
3
; (−5, 0)
Absolute minimum:
(
−3,
−4
3
2
)
No absolute maxima.
-2-
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com

©
7
j
2
N
0
E
1
J
3
z
e
K
J
u
j
t
a
a
0
k
S
U
o
b
f
1
t
I
w
j
a
P
r
b
e
g
T
L
8
L
l
C
q
.
k
A
s
A
N
l
2
l
i
O
r
r
i
v
g
h
h
T
t
P
s
s
C
r
o
e
y
s
e
e
h
r
5
v
5
e
7
d
X
.
J
C
o
M
z
a
W
d
B
e
b
a
w
U
i
P
t
7
h
J
P
I
e
n
o
f
T
i
I
n
i
i
O
t
Q
e
9
K
C
s
a
U
l
4
c
h
u
0
l
W
u
x
s
O
.
D
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
©
x
s
2
X
0
s
1
1
3
x
p
K
F
u
1
t
T
a
P
I
S
k
o
q
f
n
t
1
w
F
a
A
r
v
e
N
m
L
5
L
R
C
Z
.
h
w
m
A
h
l
D
l
S
z
r
s
i
W
g
E
h
Q
t
L
s
1
6
r
p
e
e
s
C
e
G
r
i
v
z
e
D
d
D
.
K
Finding Increasing and Decreasing Intervals
For each problem, find the open intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing.
1)
y =
−
1
5
(
x + 4
)
5
3
+
2
(
x + 4
)
2
3
− 1
2)
f
(
x
)
=
−
2
x
x − 1
3)
y =
−
3
x
x + 2
4)
y = −
x
2
5)
f
(
x
)
=
csc
(
x
)
; [
−
π,
π]
6)
f
(
x
)
=
2
x
2
− 4
x + 4
7)
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
5
+ 3
x
3
8)
f
(
x
)
=
−
(
6
x + 6
)
1
2
9)
y =
−
x
5
+ 3
x
3
+ 1
10)
y =
x
4
+ 4
x
3
+ 2
x
2
− 4
x − 5
11)
y =
−
x
5
+ 2
x
3
+ 3
12)
f
(
x
)
=
−
(
3
x − 9
)
1
3
13)
y =
x
2
+ 4
x − 2
14)
y =
−
1
6
(
x − 2
)
7
3
+
14
3
(
x − 2
)
1
3
− 2
15)
y =
2csc
(
2
x
)
; [
−
π,
π]
16)
y =
(
3
x + 12
)
1
2
17)
f
(
x
)
=
1
6
(
x − 1
)
7
3
−
14
3
(
x − 1
)
1
3
18)
f
(
x
)
=
x
4
− 4
x
2
− 2
19)
y =
x
3
+ 5
x
2
+ 3
x − 7
20)
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
2
2
− 2
x + 4

©
R
v
2
P
0
p
1
d
3
D
r
K
F
u
6
t
I
a
P
C
S
h
o
o
f
L
t
X
w
r
a
V
r
g
e
f
A
L
m
L
p
C
q
.
z
3
A
A
X
l
D
l
P
V
r
w
i
4
g
t
h
j
t
A
s
R
W
r
1
e
j
s
6
e
s
r
Z
v
b
e
L
d
F
.
y
a
A
M
X
a
0
d
U
e
f
N
w
m
i
l
t
A
h
9
k
I
R
n
V
f
A
i
U
n
r
i
5
t
T
e
K
0
C
y
a
u
l
P
c
X
u
y
l
S
u
U
s
u
.
X
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Answers to Finding Increasing and Decreasing Intervals
1) Increasing:
(
−4, 0
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞, −4
)
,
(
0,
∞
)
2) Increasing:
(
−
∞, 1
)
,
(
1,
∞
)
Decreasing: No intervals exist.
3) Increasing: No intervals exist. Decreasing:
(
−
∞, −2
)
,
(
−2,
∞
)
4) Increasing:
(
−
∞, 0
)
Decreasing:
(
0,
∞
)
5) Increasing:
(
−
π,
−
π
2
)
,
(
π
2
,
π
)
Decreasing:
(
−
π
2
, 0
)
,
(
0,
π
2
)
6) Increasing:
(
1,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞, 1
)
7) Increasing:
(
−
3 5
5
,
3 5
5
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
−
3 5
5
)
,
(
3 5
5
,
∞
)
8) Increasing: No intervals exist. Decreasing:
(
−1,
∞
)
9) Increasing:
(
−
3 5
5
,
3 5
5
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
−
3 5
5
)
,
(
3 5
5
,
∞
)
10) Increasing:
(
−1 −
2, −1
)
,
(
−1 + 2,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
−1 −
2
)
,
(
−1,
−1 + 2
)
11) Increasing:
(
−
30
5
,
30
5
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
−
30
5
)
,
(
30
5
,
∞
)
12) Increasing: No intervals exist. Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
∞
)
13) Increasing:
(
−2,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞, −2
)
14) Increasing:
(
0, 4
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞, 0
)
,
(
4,
∞
)
15) Increasing:
(
−
3
π
4
,
−
π
2
)
,
(
−
π
2
,
−
π
4
)
,
(
π
4
,
π
2
)
,
(
π
2
,
3
π
4
)
Decreasing:
(
−
π,
−
3
π
4
)
,
(
−
π
4
, 0
)
,
(
0,
π
4
)
,
(
3
π
4
,
π
)
16) Increasing:
(
−4,
∞
)
Decreasing: No intervals exist. 17) Increasing:
(
−
∞, −1
)
,
(
3,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−1, 3
)
18) Increasing:
(
− 2 , 0
)
,
(
2,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−
∞,
− 2
)
,
(
0, 2
)
19) Increasing:
(
−
∞, −3
)
,
(
−
1
3
,
∞
)
Decreasing:
(
−3,
−
1
3
)
20) Increasing:
(
−
∞, −2
)
Decreasing:
(
−2,
∞
)

Worksheet Math 124 Week 3
Worksheet for Week 3: Graphs of f(x) and f
0
(x)
In this worksheet you’ll practice getting information about a derivative from the graph
of a function, and vice versa. At the end, you’ll match some graphs of functions to graphs
of their derivatives.
If f(x) is a function, then remember that we define
f
0
(x) = lim
h→0
f(x + h) − f(x)
h
.
If this limit exists, then f
0
(x) is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at the point
(x, f(x)).
Consider the graph of f(x) below:
1. Use the graph to answer the following questions.
(a) Are there any values x for which the derivative f
0
(x) does not exist?
(b) Are there any values x for which f
0
(x) = 0?

Worksheet Math 124 Week 3
(c) This particular function f has an interval on which its derivative f
0
(x) is constant.
What is this interval? What does the derivative function look like there? Estimate
the slope of f(x) on that interval.
(d) On which interval or intervals is f
0
(x) positive?
(e) On which interval or intervals is f
0
(x) negative? Again, sketch a graph of the
derivative on those intervals.
(f) Now use all your answers to the questions to sketch a graph of the derivative function
f
0
(x) on the coordinate plane below.
Page 2

Worksheet Math 124 Week 3
2. Below is a graph of a derivative g
0
(x). Assume this is the entire graph of g
0
(x). Use the
graph to answer the following questions about the original function g(x).
g
0
(x)
(a) On which interval or intervals is the original function g(x) increasing?
(b) On which interval or intervals is the original function g(x) decreasing?
(c) Now suppose g(0) = 0. Is the function g(x) ever positive? That is, is there any x
so that g(x) 0? How do you know?
Page 3

Worksheet Math 124 Week 3
3. Six graphs of functions are below, along with six graphs of derivatives. Match the graph
of each function with the graph of its derivative.
Original Functions:
Their derivatives:
A B C
D E F
Page 4
Basic Integration Problems
I. Find the following integrals.
2
1. (5 8 5)x x dx
32
2. ( 6 9 4 3)x x x dx
3
2
3. ( 2 3)x x dx
23
8 5 6
4. dx
x
xx
1
5. ( )
3
x dx
x
5
3
3
4
6. (12 9 )x x dx
2
2
4
7.
x
dx
x
1
8. dx
xx
2
9. (1 3 )t t dt
22
10. (2 1)t dt
2
3
11. y y dy
12. d
13. 7sin( )x dx
14. 5cos( )d
15. 9sin(3 )x dx
16. 12cos(4 )d
17. 7cos(5 )x dx
18. 4sin
3
x
dx
7
19. 4
x
e dx
4
20. 9
x
e dx
21. 5cos x dx
6
22. 13
t
e dt

II. Evaluate the following definite integrals.
4
2
1
1. (5 8 5)x x dx
3
2
9
1
2. ( 2 3)x x dx
9
4
1
3. ( )
3
x dx
x
4
3
1
5
4. dx
x
2
2
1
5. (1 3 )t t dt
1
22
2
6. (2 1)t dt

Solutions
I. Find the following integrals.
3
22
5
1. (5 8 5) 4 5
3
x
x x dx x x C
4
3 2 3 2
3
2. ( 6 9 4 3) 3 2 3
2
x
x x x dx x x x C
3
2
5
2
2
2
3. ( 2 3) 3
5
x
x x dx x x C
23
23
12
2
8 5 6 8
4. 5 6
5 6 5 3
8 ( ) 8 ( )
12
dx x x dx
xx
xx
xx
Ln x Ln x C
x
x
11
22
31
31
22
22
11
5. ( )
3
3
1 2 2
31
3 3 3
22
x dx x x dx
x
xx
x x C
8
7
5
3
3
4
3
4
48 27
6. (12 9 )
78
xx
x x dx c
2
2
2
44
7. 1 4
x
dx x dx x C
x
x
3
2
12
8. dx x dx C
x x x
34
2 2 3
3
9. (1 3 ) 3
34
tt
t t dt t t dt C
53
2 2 4 2
44
10. (2 1) 4 4 1
53
tt
t dt t t dt t C

10
7
3
2
3
3
3
11.
10
y
y y dy y dy C
12. dC
13. 7sin( ) 7cos( )x dx x C
14. 5cos( ) 5sin( )dC
15. 9sin(3 ) 3cos(3 )x dx x C
16. 12cos(4 ) 3sin 4dC
7sin(5 )
17. 7cos(5 )
5
x
x dx C
18. 4sin 12cos
33
xx
dx C
7
7
4
19. 4
7
x
x
e
e dx C
44
20. 9 36
xx
e dx e C
5sin( )
21. 5cos
x
x dx C
6
6
13
22. 13
6
t
t
e
e dt C
II. Evaluate the following definite integrals.
4
3
4
22
1
1
5 188 8
1. (5 8 5) 4 5 60
3 3 3
x
x x dx x x
3
2
9
5
2
9
2
1
1
2 1026 22 1001
2. ( 2 3) 3 200.2
5 5 5 5
x
x x dx x x
9
31
9
22
4
4
1 2 2 20 40
3. ( ) 20 13.333
3 3 3 3
3
x dx x x
x
4
4
32
1
1
5 5 5 5 75
4. 2.344
32 2 32
2
dx
xx
2
34
2
2
1
1
3 44 5 57
5. (1 3 ) 14.25
3 4 3 12 4
tt
t t dt
1
53
1
22
2
2
4 4 7 254 87
6. (2 1) 17.4
5 3 15 15 5
tt
t dt t

©
d
J
2
6
0
R
1
y
3
G
H
K
v
u
W
t
a
a
A
A
S
T
o
x
f
K
t
v
w
O
a
9
r
F
e
M
L
L
y
L
D
C
v
.
2
s
e
A
b
l
u
l
d
w
r
Z
i
k
g
Q
h
V
t
W
s
b
I
r
j
e
s
s
M
e
Y
r
p
v
W
e
u
d
F
.
l
2
b
M
g
a
v
d
z
e
q
e
w
h
i
6
t
d
h
W
s
I
H
n
G
f
U
i
W
n
u
i
f
t
U
e
4
C
C
H
a
M
l
k
c
I
u
4
l
4
u
l
s
E
.
0
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
For each problem, find
F
'
(
x).
1)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−4
x
(
t − 1
)
dt 2)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−3
x
(
t
2
+ 2
t + 3
)
dt
3)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−1
x
2
(
−2
t + 2
)
dt
4)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
4
3
x
(
−
t
3
+ 11
t
2
− 39
t + 44
)
dt
5)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
2
x
3
1
t
3
dt 6)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
x
2
(
−2
t − 2
)
dt
7)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
x
2
(
t
2
− 8
t + 11
)
dt
8)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
2
x
2
t
dt

©
u
1
2
R
0
X
1
9
3
9
H
K
s
u
v
t
o
a
n
1
S
h
o
R
f
T
t
9
w
N
a
H
r
8
e
m
W
L
N
L
k
C
Q
.
J
h
N
A
t
l
B
l
1
q
r
x
i
m
g
N
h
2
t
G
s
M
J
r
I
e
o
s
o
e
C
r
4
v
2
e
o
d
N
.
L
Z
9
M
a
a
p
d
n
e
T
h
w
a
i
X
t
d
h
r
z
I
v
n
J
f
x
i
z
n
f
i
q
t
V
e
X
d
C
a
a
t
l
h
c
S
u
9
l
h
u
e
s
7
.
I
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
For each problem, find
F
'
(
x).
1)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−4
x
(
t − 1
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
x − 1
2)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−3
x
(
t
2
+ 2
t + 3
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
x
2
+ 2
x + 3
3)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
−1
x
2
(
−2
t + 2
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
−4
x
3
+ 4
x
4)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
4
3
x
(
−
t
3
+ 11
t
2
− 39
t + 44
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
−81
x
3
+ 297
x
2
− 351
x + 132
5)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
2
x
3
1
t
3
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
3
x
7
6)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
x
2
(
−2
t − 2
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
−4
x
3
− 2
x + 2
7)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
x
2
(
t
2
− 8
t + 11
)
dt
F
'
(
x
)
=
2
x
5
− 16
x
3
−
x
2
+ 30
x − 11
8)
F
(
x
)
=
∫
x
2
x
2
t
dt
F
'
(
x
)
= 0
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com

©
c
0
2
N
0
E
1
p
3
R
a
K
t
u
a
t
h
a
8
N
S
y
o
o
f
d
t
V
w
r
a
a
r
w
e
q
W
L
t
L
x
C
b
.
S
Z
t
A
F
l
G
l
k
t
r
2
i
v
g
w
h
l
t
a
s
Z
w
r
i
e
e
s
N
e
r
r
J
v
Y
e
s
d
A
.
E
o
P
M
U
a
t
d
s
e
i
G
w
3
i
f
t
g
h
D
a
I
K
n
e
f
Y
i
n
n
8
i
E
t
D
e
L
Z
C
Y
a
N
l
d
c
o
u
T
l
m
u
L
s
J
.
b
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Integration by Substitution
Evaluate each indefinite integral. Use the provided substitution.
1)
∫
−15
x
4
(
−3
x
5
− 1
)
5
dx;
u =
−3
x
5
− 1 2)
∫
−16
x
3
(
−4
x
4
− 1
)
−5
dx;
u =
−4
x
4
− 1
3)
∫
−
8
x
3
(
−2
x
4
+ 5
)
5
dx;
u =
−2
x
4
+ 5
4)
∫
(
5
x
4
+ 5
)
2
3
⋅ 20
x
3
dx;
u =
5
x
4
+ 5
5)
∫
(
5 + ln
x
)
5
x
dx;
u =
5 + ln
x
6)
∫
4sec
4
x ⋅ tan
4
x ⋅
sec
4
4
x
dx;
u = sec
4
x
7)
∫
36
x
3
(
3
x
4
+ 3
)
5
dx;
u =
3
x
4
+ 3 8)
∫
x
(
4
x − 1
)
4
dx;
u =
4
x − 1
-1-

©
L
f
2
v
0
S
1
z
3
U
N
K
Y
u
1
t
P
a
1
T
S
9
o
3
f
V
t
7
w
U
a
z
r
p
e
T
C
L
p
L
b
C
G
.
T
T
7
A
f
l
Y
l
w
d
r
i
i
T
g
N
h
0
t
n
s
U
J
r
Q
e
V
s
j
e
B
r
1
v
I
e
c
d
g
.
p
g
r
M
K
a
L
d
z
e
G
f
w
r
i
E
t
G
h
K
l
I
3
n
c
f
X
i
K
n
8
i
y
t
Z
e
0
9
C
5
a
Y
l
B
c
R
u
1
l
r
u
8
s
i
.
p
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Evaluate each indefinite integral.
9)
∫
−9
x
2
(
−3
x
3
+ 1
)
3
dx 10)
∫
12
x
3
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
4
dx
11)
∫
−12
x
2
(
−4
x
3
+ 2
)
−3
dx
12)
∫
(
3
x
5
− 3
)
3
5
⋅ 15
x
4
dx
13)
∫
(
−2
x
4
− 4
)
4
⋅ −32
x
3
dx
14)
∫
(
e
4
x
− 4
)
1
5
⋅
8
e
4
x
dx
15)
∫
x
(
4
x + 5
)
3
dx 16)
∫
5
x
2
x + 3
dx
-2-

©
4
v
2
S
0
z
1
y
3
Z
0
K
0
u
V
t
x
a
f
l
S
2
o
R
f
6
t
n
w
b
a
C
r
K
e
a
n
L
X
L
1
C
M
.
m
A
J
A
T
l
P
l
4
B
r
k
i
R
g
B
h
X
t
x
s
Z
b
r
v
e
G
s
G
e
N
r
y
v
D
e
r
d
j
.
9
L
q
M
M
a
w
d
h
e
V
5
w
k
i
z
t
b
h
X
L
I
Q
n
B
f
l
i
b
n
Z
i
J
t
F
e
I
G
C
X
a
L
l
V
c
O
u
q
l
E
u
W
s
C
.
v
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Kuta Software - Infinite Calculus Name___________________________________
Period____Date________________
Integration by Substitution
Evaluate each indefinite integral. Use the provided substitution.
1)
∫
−15
x
4
(
−3
x
5
− 1
)
5
dx;
u =
−3
x
5
− 1
1
6
(
−3
x
5
− 1
)
6
+
C
2)
∫
−16
x
3
(
−4
x
4
− 1
)
−5
dx;
u =
−4
x
4
− 1
−
1
4
(
−4
x
4
− 1
)
4
+
C
3)
∫
−
8
x
3
(
−2
x
4
+ 5
)
5
dx;
u =
−2
x
4
+ 5
−
1
4
(
−2
x
4
+ 5
)
4
+
C
4)
∫
(
5
x
4
+ 5
)
2
3
⋅ 20
x
3
dx;
u =
5
x
4
+ 5
3
5
(
5
x
4
+ 5
)
5
3
+
C
5)
∫
(
5 + ln
x
)
5
x
dx;
u =
5 + ln
x
1
6
(
5 + ln
x
)
6
+
C
6)
∫
4sec
4
x ⋅ tan
4
x ⋅
sec
4
4
x
dx;
u = sec
4
x
1
5
⋅
sec
5
4
x +
C
7)
∫
36
x
3
(
3
x
4
+ 3
)
5
dx;
u =
3
x
4
+ 3
1
2
(
3
x
4
+ 3
)
6
+
C
8)
∫
x
(
4
x − 1
)
4
dx;
u =
4
x − 1
1
96
(
4
x − 1
)
6
+
1
80
(
4
x − 1
)
5
+
C
-1-

©
B
v
2
9
0
y
1
d
3
6
7
K
Y
u
v
t
r
a
1
W
S
T
o
0
f
v
t
3
w
O
a
B
r
R
e
R
f
L
D
L
G
C
f
.
u
8
q
A
G
l
6
l
3
v
r
c
i
2
g
X
h
e
t
6
s
x
Q
r
G
e
f
s
9
e
I
r
C
v
K
e
b
d
G
.
G
O
a
M
p
a
T
d
y
e
q
x
w
O
i
1
t
p
h
2
t
I
F
n
H
f
M
i
I
n
m
i
F
t
Q
e
E
b
C
m
a
o
l
8
c
o
u
d
l
y
u
O
s
P
.
J
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
Evaluate each indefinite integral.
9)
∫
−9
x
2
(
−3
x
3
+ 1
)
3
dx
1
4
(
−3
x
3
+ 1
)
4
+
C
10)
∫
12
x
3
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
4
dx
1
5
(
3
x
4
+ 4
)
5
+
C
11)
∫
−12
x
2
(
−4
x
3
+ 2
)
−3
dx
−
1
2
(
−4
x
3
+ 2
)
2
+
C
12)
∫
(
3
x
5
− 3
)
3
5
⋅ 15
x
4
dx
5
8
(
3
x
5
− 3
)
8
5
+
C
13)
∫
(
−2
x
4
− 4
)
4
⋅ −32
x
3
dx
4
5
(
−2
x
4
− 4
)
5
+
C
14)
∫
(
e
4
x
− 4
)
1
5
⋅
8
e
4
x
dx
5
3
(
e
4
x
− 4
)
6
5
+
C
15)
∫
x
(
4
x + 5
)
3
dx
1
80
(
4
x + 5
)
5
−
5
64
(
4
x + 5
)
4
+
C
16)
∫
5
x
2
x + 3
dx
1
2
(
2
x + 3
)
5
2
−
5
2
(
2
x + 3
)
3
2
+
C
-2-
Create your own worksheets like this one with
Infinite Calculus
. Free trial available at KutaSoftware.com
